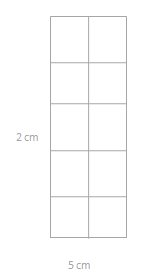
Fun learning activities are the best option to educate primary school students and make them understand the basic mathematical concepts like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. Grade 3 primary school students can find these fun-learning exercises for all math concepts through the Eureka Math Answers Grade 3 Common Core Curriculum.
Engage NY Eureka Math 3rd Grade Module 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key
You may have diverse opportunities to develop math skills and problem-solving skills but practicing with Eureka Math 3rd Grade Answer Key for better and efficient learning. Eureka Math Grade 3 provided Free Access Student Edition of Eureka Math Grade 3 Answers are enough to practice more and get a good grip on the subject. The diverse opportunities will develop problem-solving skills among the primary school kids Practising.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 12 Pattern Sheet Answer Key
Multiply
Answer:
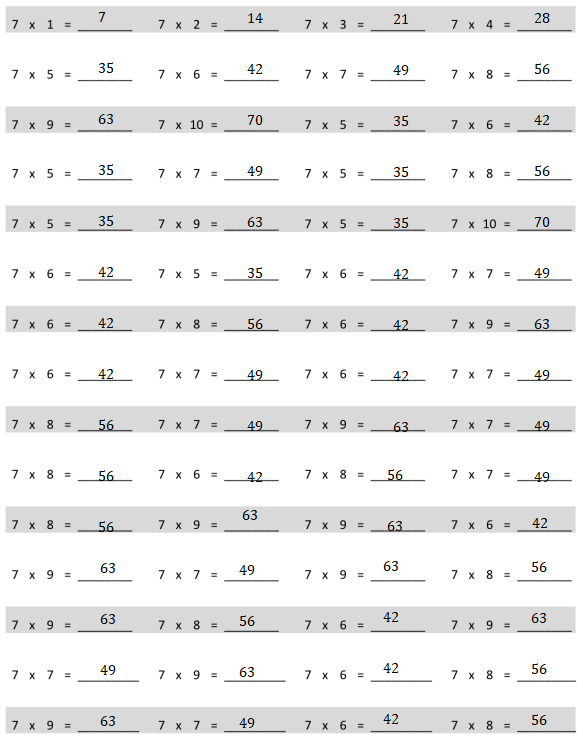
7 x 1 = 7, 7 x 2 = 14, 7 x 3 = 21, 7 x 4 = 28, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 10 = 70, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 10 = 70, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 52, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
multiply with 7.
7 x 1 = 7, 7 x 2 = 14, 7 x 3 = 21, 7 x 4 = 28, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 10 = 70, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 10 = 70, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 5 = 35, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 52, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56, 7 x 9 = 63, 7 x 7 = 49, 7 x 6 = 42, 7 x 8 = 56.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 12 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
Each side on a sticky note measures 9 centimeters. What is the area of the sticky note?
Answer:
The area of sticky notes = 81 sq cm.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the area of the sticky notes = 81 sq cm.
area = l x b.
where l = length, and b = breadth.
area = 9 x 9.
area = 81.
so the area of the sticky notes = 81 sq cm.
Question 2.
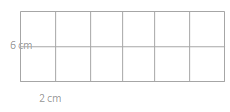
Stacy tiles the rectangle below using her square pattern blocks.
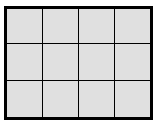
a. Find the area of Stacy’s rectangle in square units. Then, draw and label a different rectangle with whole number side lengths that has the same area.
Answer:
The area of the stacky tiles = 12 sq units.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the area of the rectangle = l x b.
where l = length, b = breadth.
area = l x b.
area = 3 x 4.
area = 12 sq units.
so the area of the stacky tiles = 12 sq units.
b. Can you draw another rectangle with different whole number side lengths and have the same area? Explain how you know.
Answer:
The area of the rectangle = 12 sq units.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the area of the rectangle = l x b.
where l = length, b = breadth.
area = l x b.
area = 2 x 6.
area = 12 sq units.
so the area of the other rectangle = 12 sq units.

Question 3.
An artist paints a 4 foot × 16 foot mural on a wall. What is the total area of the mural? Use the break apart and distribute strategy.

Answer:
The area of the mural on a wall = 64 sq ft.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
An artist paints a 4-foot x 16 foot mural on a wall.
area = 4 x 16.
area = 4 x ( 10 + 6 ).
area = ( 4 x 10 ) + 6.
area = 40 + 6.
area = 46.
so the area of the mural on a wall = 64 sq ft.
Question 4.
Alana tiles the 3 figures below. She says, “I’m making a pattern!”
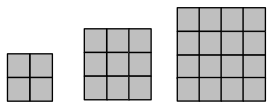
a. Find the area of Alana’s 3 figures and explain her pattern.
Answer:
The area of the square 1 = 4 sq units.
the area of the square 2 = 9 sq units.
the area of the square 3 = 16 sq units.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Alana tiles the 3 figures.
the area of the square 1 = 4 sq units.
area = l x b.
where l = length, b = breadth.
area = 2 x 2.
area = 4.
the area of the square 2 = 9 sq units.
area = l x b.
area = 3 x 3.
area = 9.
the area of the square 3 = 16 sq units.
area = l x b.
area = 4 x 4.
area = 16.
b. Draw the next 2 figures in Alana’s pattern and find their areas.
Answer:
The area of square 1 = 25 sq units.
the area of square 2 = 36 sq units.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Alana tiles the 3 figures.
the area of the square 1 = 25 sq units.
area = l x b.
where l = length, b = breadth.
area = 5 x 5.
area = 25.
the area of the square 2 = 36 sq units.
area = l x b.
area = 6 x 6.
area = 36.
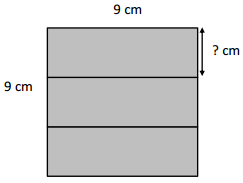
Question 5.
Jermaine glues 3 identical pieces of paper as shown below and makes a square. Find the unknown side length of 1 piece of paper. Then, find the total area of 2 pieces of paper.
Answer:
The unknown side length of 1 piece of paper = 3 cm.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Jermaine glues 3 identical pieces of paper as shown below and makes a square.
area of the rectangle = 3 x 3cm.
area = 3 x 3.
area = 9 cm.
so the unknown side length of 1 piece of paper = 3 cm.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 12 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
A painting has an area of 63 square inches. One side length is 9 inches. What is the other side length?
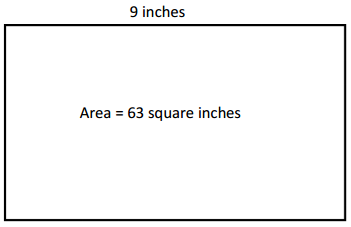
Answer:
The other side length of the rectangle = 7 inches.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
A painting has an area of 63 square inches.
one side length is 9 inches.
area of the rectangle is given.
63 = l x b.
l = 9 inches.
63 = 9 x b.
b = 63 / 9.
b = 7 inches.
so the other side length of the rectabgle = 7 inches.
Question 2.
Judy’s mini dollhouse has one floor and measures 4 inches by 16 inches. What is the total area of the dollhouse floor?
Answer:
The total area of the dollhouse floor = 64 sq inches.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Judy’s mini dollhoue has one floor and measures 4 inches by 16 inches.
area = l x b.
where l = length, and b = breadth.
area = 4 x 16.
area = 64 sq inches.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 12 Homework Answer Key
Question 1.
A square calendar has sides that are 9 inches long. What is the calendar’s area?
Answer:
The area of the square calendar = 81 sq inches.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
A square calendar has sides that are 9 inches long.
area = l x b.
where l = length and b = breadth.
area = 9 x 9 = 81 sq inches.
so the area of the square calendar = 81 sq inches.
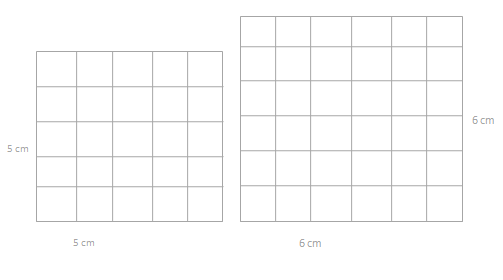
Question 2.
Each 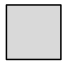 is 1 square unit. Sienna uses the same square units to draw a 6 × 2 rectangle and says that it has the same area as the rectangle below. Is she correct? Explain why or why not.
is 1 square unit. Sienna uses the same square units to draw a 6 × 2 rectangle and says that it has the same area as the rectangle below. Is she correct? Explain why or why not.
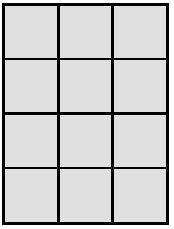
Answer:
Yes, she was correct.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Sienna uses the same square units to draw a 6 x 2 rectangle.
area of the given rectangle = 12 sq units.
area = 4 x 3.
area = 12 sq units.
area of Sienna’s rectangle = 12 sq units.
area = 6 x 2.
area = 12 sq units.
Question 3.
The surface of an office desk has an area of 15 square feet. Its length is 5 feet. How wide is the office desk?
Answer:
The width of the office desk = 3 feet.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
The surface of an office desk has an area of 15 square feet.
Its length is 5 feet.
area = l x w.
15 = 5 x w.
w = 15 / 5.
w = 3 feet.
so the width of the office desk = 3 feet.
Question 4.
A rectangular garden has a total area of 48 square yards. Draw and label two possible rectangular gardens with different side lengths that have the same area.
Answer:
The side lengths of the rectangular garden 1 = 6 x 8 yards.
The side lengths of the rectangular garden 2 = 12 x 4 yards.
Explanation:
given that,
A rectangular garden 1 has a total area of 48 square yards.
area = l x b.
where l = length and b = breadth.
area = 6 x 8 = 48 sq yards.
so the area of the rectangular garden 1 = 48 sq yards.
A rectangular garden 2 has a total area of 48 square yards.
area = l x b.
where l = length and b = breadth.
area = 12 x 4 = 48 sq yards.
so the area of the rectangular garden 2 = 48 sq yards
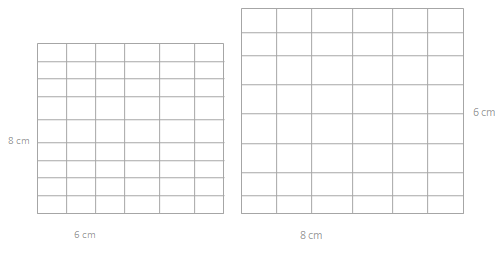
Question 5.
Lila makes the pattern below. Find and explain her pattern. Then, draw the fifth figure in her pattern
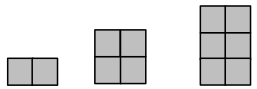
Answer:
The area of the square 1 = 2 sq units.
the area of the square 2 = 4 sq units.
the area of the square 3 = 6 sq units.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Alana tiles the 3 figures.
the area of the square 1 = 2 sq units.
area = l x b.
where l = length, b = breadth.
area = 1 x 2.
area = 2.
the area of the square 2 = 4 sq units.
area = l x b.
area = 2 x 2.
area = 4.
the area of the square 3 = 6 sq units.
area = l x b.
area = 3 x 2.
area = 6.