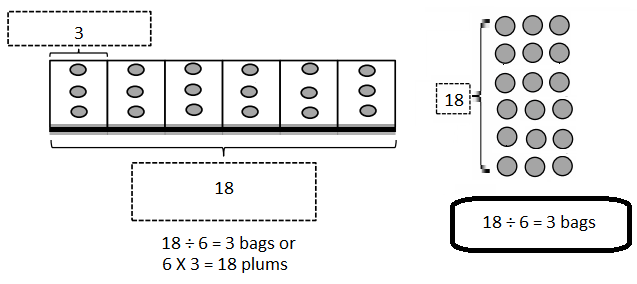
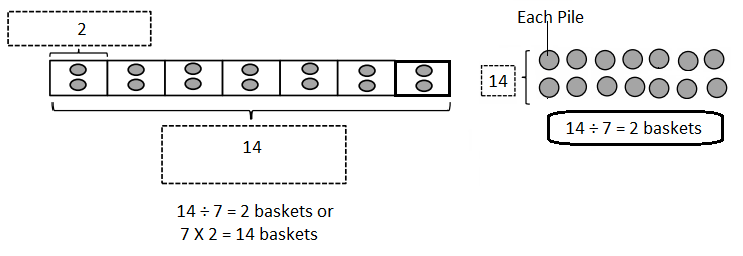
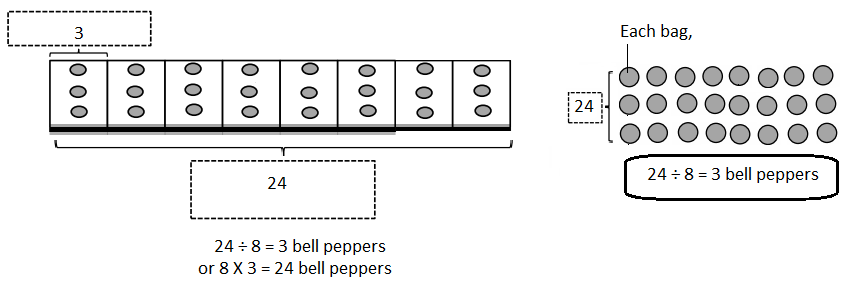
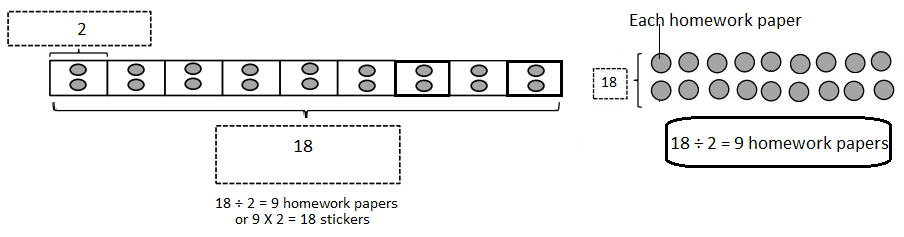
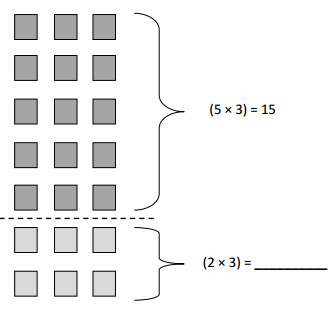
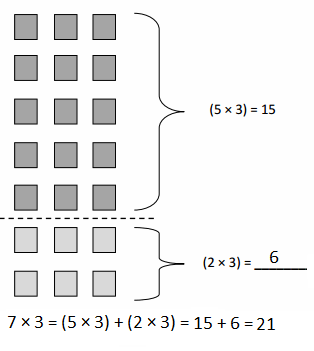
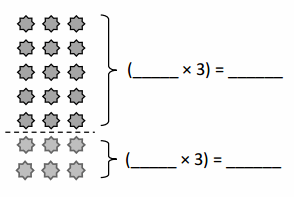
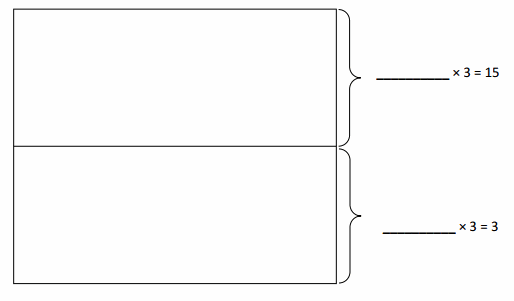
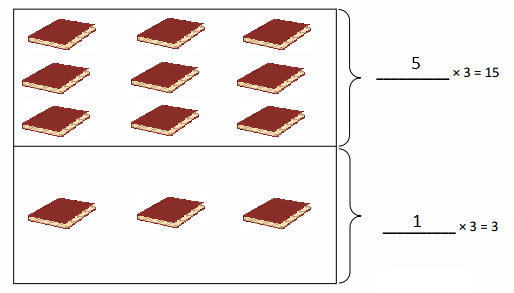
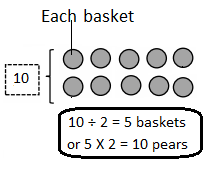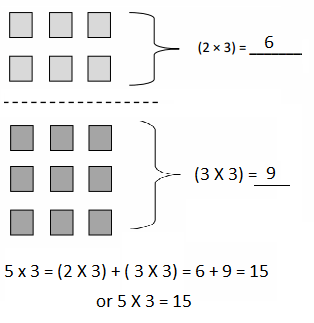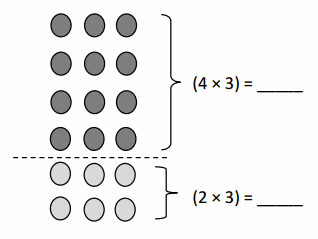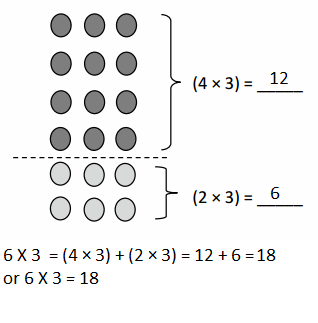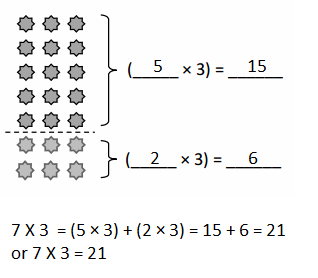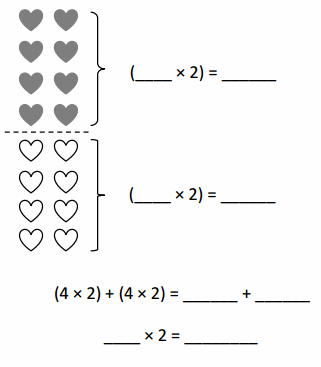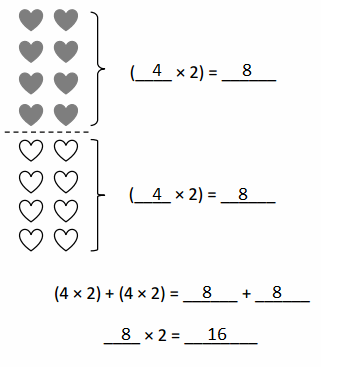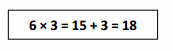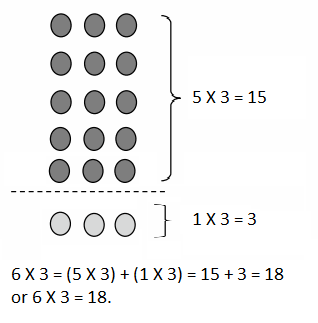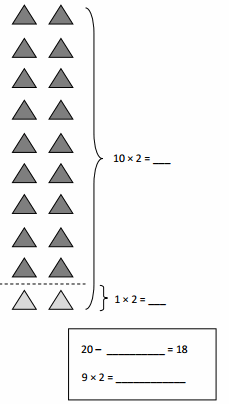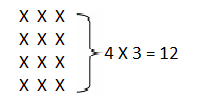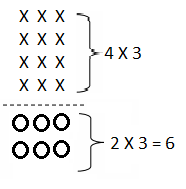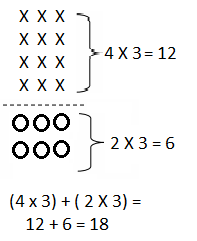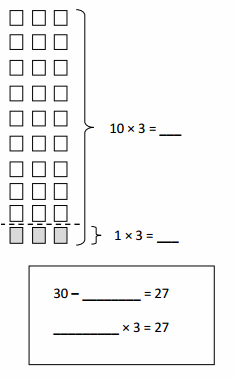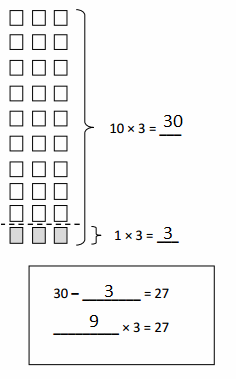Do you want practical learning with real-time examples? Then, refer to Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts. You can easily enhance your skills by practicing the problems from Big Ideas Math Answer Key, Grade 5 Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts. Be the first to access Big Ideas Grade 5 Chapter 1 Math Answers PDF to start your practice. Check out each topic available on the below math answers. Every topic is given individually along with answers and explanations. It is easy to become a topper in the exam by practicing with the Big Ideas Grade 5 Math Answers Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts.
Big Ideas 5th Grade Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts Math Book Answer Key
Students can learn the quick way to solve problems using Big Ideas Grade 5 Chapter 1 Math Answers. Download Grade 5 Big Ideas Math Answers Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts for free. We provided solutions in an easy manner so that students can solve the problems in less time. Click on the links provided below and find every topic individually. Get the free pdf offline and practice whenever you want it.
Lesson 1: Place Value Patterns
Lesson 2 Place Value with Whole Numbers
Lesson 3 Patterns and Powers of 10
Lesson 4 Decimals to Thousandths
Lesson 5 Place Value with Decimals
Lesson 6 Compare Decimals
Lesson 7 Round Decimals
Performance Task
Lesson 1.1 Place Value Patterns
Explore and Grow
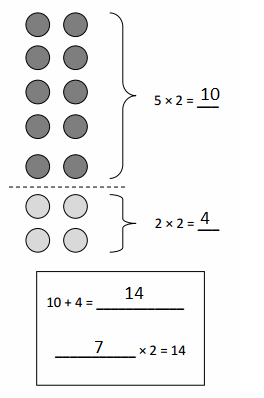
Write the whole number represented by each base ten block. Then use the base ten blocks to complete the table.
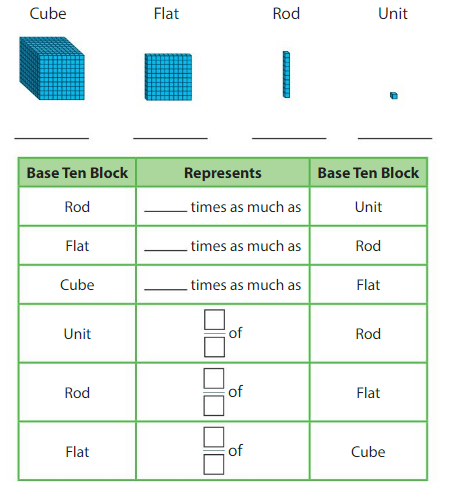
Answer:
Rod is 10 times as much as Unit
The flat is 10 times as much as Rod
Cube is 3 times as much as Flat
Unit is 1/10 of Rod
Rod is 1/10 of Flat
The flat is 3/10 of Cube
Reasoning
Describe the patterns you see in a number as you move from one place value position to another place value position.
Answer: As we move from one place value position to another value position, The place value of a digit increase by ten times as move from the left.
Think and Grow: Place Value Patterns
You can use a place value chart to help write numbers that are 10 times as great as a number or \(\frac{1}{10}\) of a number.
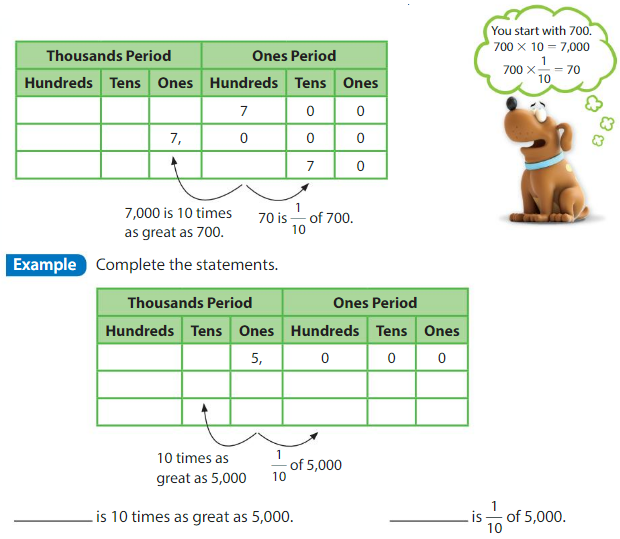
Show and Grow
Question 1.
Complete the statements.
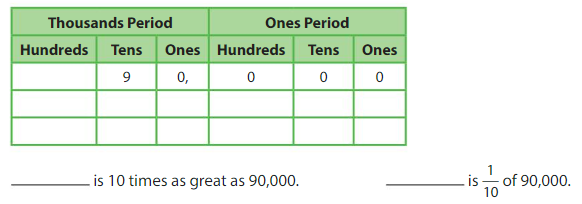
Apply and Grow: Practice
Use a place value chart to answer the question.
Question 2.
What number is 10 times as great as 6,000?
Answer:60,000
If 6,000 is multiplied by 10 times it becomes 60,000
Question 3.
What number is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 300?
Answer:30
300 x 1/ 10 is 30
Question 4.
80 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer: 8
if 8 is multiplied by 10 times it becomes 80
Question 5.
40,000 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:4,00,000
4,00,000 x 1/10 is 40,000
The number is 4,00,000
Complete the table.
Question 6.
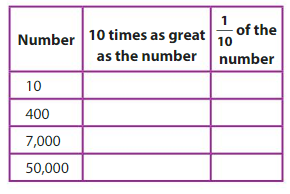
Answer:
1. 100 ,1 ,
10, 10 times as number is 10 x 10 = 100
1/10 of 10 is 1
2. 4000,40
400, 10 times as number is 400 x 10 = 4000
1/10 of 400 is 40
3. 70,000,700
7,000, 10 times as number is 7,000 x 10 =70,000
1/10 of 7,000 is 700
4. 500,000, 5,000
50,000,10 times as number is 50,000 x 10 = 5,00,000
1/10 of 50,000 is 5,000
Question 7.
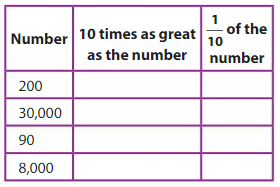
Answer:
1. 2,000, 20
200, 10 times as number is 200 x 10 = 2,000
1/10 of 200 is 20
2. 3,00,000, 3,000
30,000, 10 times as number is 30,000 x 10 = 3,00,000
1/10 of 30,000 is 3,000
3. 900, 9
90, 10 times as number is 90 x 10 = 900
1/10 of 90 is 9
4. 80,000, 800
8,000, 10 times as number is 8,0,0 x 10 = 80,000
1/10 of 8,000 is 800
Question 8.
Patterns
Describe the relationship between any place value position and the next greater place value position.
Answer:
The relation between any place value position and next greater place value position increases ten times as we move.
Number Sense
Write whether the statement is true or false. If false, explain why.
Question 9.
600 is 100 times as great as 60,000.
______
Answer: True
600 X 100 = 60,000
Question 10.
9,000 is 1,000 times as great as 9.
_____
Answer: True
9 X 1,000 = 9,000
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
Which state is about 10 times larger than Georgia?
The approximate land area of Georgia is 60,000 square miles.
Use a place value chart to find the number that is 10 times as great as 60,000.
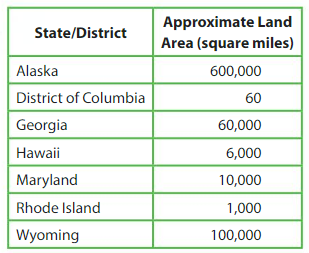
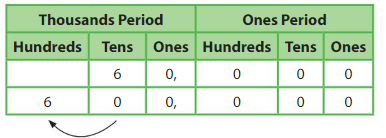
6,000_____ is 10 times as great as 60,000.
The land area of _____Alaska__ is about 600,000 square miles.
So, __Alaska____ is about 10 times larger than Georgia.
Show and Grow
Use the table above.
Question 11.
Which state is about 10 times larger than Hawaii?
Answer: Georgia is 10 times larger than Hawaii
Question 12.
Which state is about \(\frac{1}{10}\) the size of Wyoming?
Answer: Maryland is 1/10 the size of Wyoming
Question 13.
DIG DEEPER!
Which state is about 100 times larger than the District of Columbia?
Answer: Hawaii
District of Columbia = 60
100 times larger than the District of Columbia 60 X 100 = 6,000 is Hawaii
Question 14.
DIG DEEPER!
A mother rhinoceros weighs 2 tons. Her baby weighs \(\frac{1}{10}\) as much as her. What is the weight of the baby rhinoceros, in pounds.

Answer: The weight of the baby rhinoceros is 20 Pounds.
2 tons Mother
Baby = 200 x 1/10 = 20 Pounds
Place Value Patterns Homework & Practice 1.1
Complete the statements.
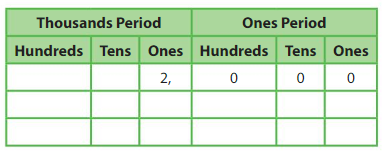
Question 1.
______ is 10 times as great as 2,000.
Answer: 20,000
2,000 x 10 = 20,000
Question 2.
_____ is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 2,000.
Answer: 200
2,000 x 1/ 10 = 200
Use a place value chart to answer the question.
Question 3.
What number is 10 times as great as 50?
Answer: 500
50 x 10 = 500
Question 4.
What number is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 4,000?
Answer: 400
4,000 x 1/10 = 400
Question 5.
800 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:8,000
8,000 x 1/10 = 800
Question 6.
60,000 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer:6,000
6,000 is 10 times means 6,000 x 10 =60,000
Complete the table.
Question 7.
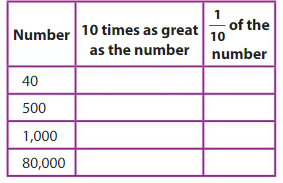
Answer:
1. 400, 4
40, 10 times as number is 40 x 10 = 400
1/10 of 40 is 4
2. 5,000, 50
500, 10 times as number is 500 x 10 = 5,000
1/10 of 500 is 50
3. 10,000 , 100
1,000, 10 times as number is 1,000 x 10 = 10,000
1/10 of 1,000 is 100
4.8,00,000 , 8,000
80,000, 10 times as number is 80,000 x 10 = 8,00,000
1/10 of 80,000 is 8,000
Question 8.
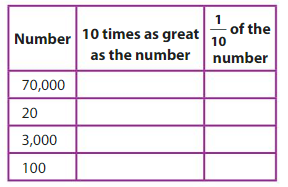
Answer:
1. 7,00,000 , 7,000
70,000, 10 times as number is 70,000 x 10 = 7,00,000
1/10 of 70,000 is 7,000
2. 200 , 2
20, 10 times as number is 20 x 10 = 200
1/10 of 20 is 2
3. 30,000, 300
3,000, 10 times as number is 3,000 x 10 = 30,000
1/10 of 3000 is 300
4. 1,000 , 10
100, 10 times as number is 100 x 10 = 1,000
1/10 of 100 is 10
Question 9.
Patterns
Describe the relationship between any place value position and the next lesser place value position.
Answer:
The relation between any place value position and next lesser place value position decreases ten times as we move.
Question 10.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says 6,700 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 67,000. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: Yes My friend is correct, because if we divide 67,000 by 10 we get the result as 6,700 only.
Use the table.
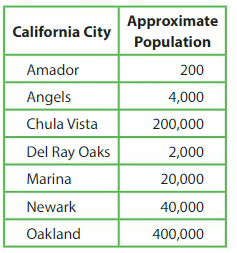
Question 11.
Modeling Real Life
Which city’s population is about 10 times the population of Newark?
Answer: Population of Oakland.
Newark=40,000
40,000 x 10 = 4,00,000 is Oakland
Question 12.
Modeling Real Life
Which city’s population is about \(\frac{1}{10}\) the population of Marina?
Answer: Population of Del Ray Oaks.
Marina = 20,000
20,000 x 1/10 = 2,000=Del Ray Oaks
Question 13.
DIG DEEPER!
An archaeologist finds a ceramic bowl that is about 400,000 years old. He finds different artifact that is \(\frac{1}{100}\) times as old as the 100ceramic bowl. How much older is the ceramic bowl than the other artifact?
Answer: The Ceramic bowl is 4000 years old.
4,00,000 x 1/100= 4,000
Review & Refresh
Find the factor pairs for the number.
Question 14.
9
Answer: 1,3,9 are factor pairs of 9
Question 15.
24
Answer: (1,24), (2,12) (3,8) and (4,6) are factor pairs of 24
Question 16.
15
Answer:(1,3,5,15) are factor pairs of 15
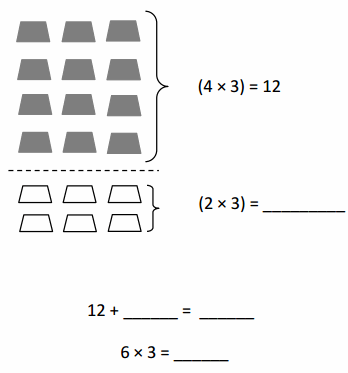
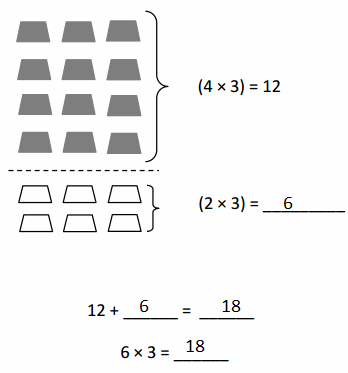
Lesson 1.2 Place Value with Whole Numbers
Model the number. Draw your model.
Then write the value of each digit.

Compare the values of the 4s.
Answer: Thousands-4, Hundreds -4 , Tens – 4 and Ones- 2
4 is in thousand, 4 is in Hundreds and 4 is at tens value.
Repeated Reasoning
Is the value of the 4 in the tens place 10 times as much as the value of the 2 in the ones place? Explain.
Answer: No, Why means 4 in tens place means its value is 40 and 2 in ones place means only 2so 4 in the tens place is not 10 times as the value of 2.
Think and Grow: Place Value with Whole Numbers
Key Idea
A place value chart shows the value of each digit in a number. It also shows how the place values are grouped. Each group of three digits is called a period. Ina number, periods are separated by commas.
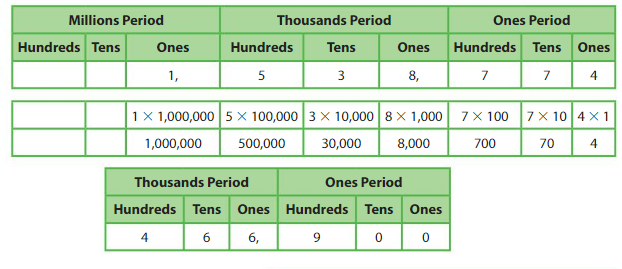
Example
Write the number in standard form, word form, and expanded form.
Standard form:4,66,900
Word form: Four hundreds sixty six thousand and nine hundred
Expanded form:
4 × 1,00,000 + __6___ × 10,000_____ + ___6__ × _1,000_____ + _9____ × __100____
Show and Grow
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 1.
Standard form: 78,300
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word Form : Seventy -Eight Thousand, Three Hundred.
Expanded Form : 7 x 10,000 + 8 x 1000 + 3 x 100=78,300
Question 2.
Standard form:
Word form: three hundred fifty thousand, fifty-eight
Expanded form:
Answer:
Standard Form : 300,50,058
Expanded Form : 3 x 10,00,000+ 5 x 10,000 + 5 x 10 +8=300,50,058
Question 3.
Compare the values of the 6s in the number 466,900.
Answer:
the values of the 6 s are one is in 60 thousand’s place and other is at 6 thousands place.
Apply and Grow: Practice
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 4.
Standard form:
Word form:
Expanded form: 6 × 100,000 + 8 × 1,000 + 4 × 100 + 5 × 10 + 9 × 1
Answer:
Standard Form : 6,08,459
Word Form : 6 hundred / six lakh, eight thousand , four hundred fifty nine.
Question 5.
Standard form: 45,006,702
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: forty five lakh ,six thousand seven hundred and two.
Expanded form:4 x 10000000 + 5 x 1000000 + 6 x 1000 +
7 x 100 +2
Question 6.
Compare the values of the 7s in the number 4,877,034.
Answer:
The value’s of 7s is at seventy thousand,(70,000) and again at seven thousand(7,000).
Question 7.
Compare the values of the 3s in the number 5,338.
Answer:
The values of 3s is at 3-Hundred(300) and at thirty (30)[3 tens)]
or
3 at hundreds and 3 at tens place.
Compare.
Question 8.
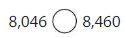
Answer:
In 8,046 The value of 4 is in Ten’s place and 6 is in one’ s place
and in 8,460 the value of 4 is in hundreds place and 6 in ten’s place.
Question 9.
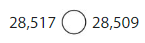
Answer:
In 28,517 the value of 2 is at twenty thousand place, 8 at thousands and 5 at hundreds, 1 at tens and 7 at one’s place.
and 28,509 the value of 2 is at twenty thousand place, 8 at thousands and 5 at hundreds, zero at tens and 9 at one’s place.
Question 10.
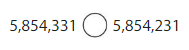
Answer:
In 5,854,331- Fifty Lakhs , 8 at lakhs, Five at ten thousand, 4 at thousand,3 at hundred, 3 at ten’s and 1 at one’s place.
and in 5,854,231 – Fifty Lakhs , 8 at lakhs, Five at ten thousand, 4 at thousand,2 at hundred, 3 at ten’s and 1 at one’s place.
Question 11.
The white truffle is the world’s most expensive edible fungus, which costs up to three thousand dollars per kilogram. Write this number in standard form.

Answer:
Standard Form: 3000$ per Kg.
the white truffle is 3000$ per kg.
Question 12.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says that in the number 45,951, one 5 is 10 times as great as the other 5. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, because at first the 5 is at tens place and in next time 5 is at thousands place so friend is right 5 is 10 times greater as the other 5 . As we move from right value to left twice tens value place becomes thousand value place.
Question 13.
Logic
Newton is thinking of a 6-digit number in which all of the digits are the same. The value of the digit in the thousands place is 8,000. What is Newton’s number?
Answer:
8,88,888
8 x 1,00,000 + 8 x 10,000+8 x 1,000+8 x 100 + 8 x 10 + 8 x 1
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
Compare the values of the 3sin Jupiter’s average distance from the Sun.
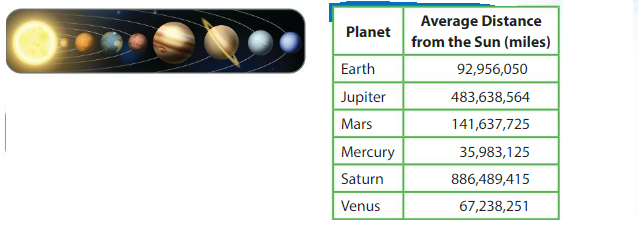
Use a place value chart to help you find the value of each 3.
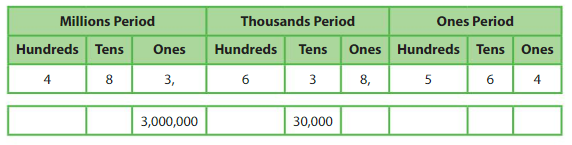
Each place value is 10 times as great as the place value to its right. The digits are two places apart. So, multiply 30,000 by 10 × 10 = 100.
So, the value of the 3 in the millions place is _______ times the value of the 3 in the ten thousands place.
Show and Grow
Use the table above.
Question 14.
Compare the values of the 7s in Mars’s average distance from the Sun.
Answer:
the value of 7 s in first is in thousands place and next 7 s is at hundreds place, the digits are one place apart, so the value of first 7 is in thousands place is 10 times the value of the next 7s in hundreds place.
Question 15.
Compare the values of the 4s in Saturn’s average distance from the Sun.
Answer:
the value of 4 s in first is in four hundred thousands place and next 4 s is at hundreds place, the digits are two places apart, so the value of first 4 is in hundred thousands place is 100 times the value of the next 4s in hundreds place.
Question 16.
DIG DEEPER!
An organization wants to donate all of the money raised through fund raisers and raffles to a children’s charity. Complete the donation check.
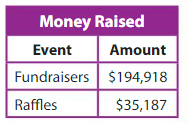

Answer:
1.
$ 194,918 + $ 35,187 = $ 230,005
Word Form : Two Hundred, Thirty thousand and Five dollars.
Standard Form : $ 230,005
Place Value with Whole Numbers Homework & Practice 1.2
Write the value of the underlined digit.
Question 1.
740,225
Answer:
4 is at Forty thousand place
Question 2.
604,197,872
Answer:
6 is at Six Hundred Lakh place
Question 3.
12,405,287
Answer:
2 is at twenty Lakh or twenty hundred thousand place
Question 4.
392,183
Answer:
3 is at 3 lakhs or 3 hundred thousand place
9 is at ninety thousand place
2 is at 2 thousand place
1 is at one hundred place
8 is at eighty place
3 is at ones place place
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 5.
Standard form: 450,014
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word Form : 4 lakhs or 4 hundred thousand , fifty thousand and fourteen
Expanded Form : 4 x 1,00,000 +5 x 10000 + 1 x 10 + 4
Question 6.
Standard form:
Word form: fourteen thousand, two hundred one
Expanded form:
Answer:
Standard Form : 14,201
Expanded Form : 1 X 10000 + 4 X 1000 + 2 X 100 +1
Question 7.
Compare the values of the 9s in the number 537,499.
Answer:
First 9 is at ones place, and second 9 is at tens place.
Question 8.
Compare the values of the 5s in the number 78,550,634.
Answer:
First 5 is at Ten Thousands place,
Second 5 is at Five Hundred Thousands place.
Compare.
Question 9.

Answer:
67,893 < 67,943
6 at sixty thousand place ,6 at sixty thousand place
7 at thousand place, 7 at thousand place
8 at eight hundred place,9 at nine hundred is great
9 at tens place and 4 at four at tens place is less
and 3 at ones place and 3 at ones place is same
Question 10.
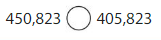
Answer:
450,823 > 405,823
4 at Four hundred thousand,
5 at fifty thousand and 0 is smaller at ten thousands place
0 at thousands place is smaller than 5 at thousands place
8 at hundreds place is same as 8 at hundreds place
2 at tens place is same as 2 at tens place
and 3 at ones place is same as 3 at ones place
Question 11.
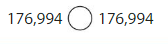
Answer:
176,994 = 176,994
1 at one hundred thousand, is same at 1 at One Hundred Thousand place
7 at Seventy thousand is same at 7 at Seventy Thousand place
6 at six thousand is same at 6 at six thousand place
9 at hundreds place is same at 9 at hundreds place
9 at ninety or 9 tens place is same as 9 at Ninety or 9 Tens place
and 4 at ones place is same as 4 at Ones place
Question 12.
Your body contains about 60,000 miles of blood vessels. Write this number in word form.
Answer:
60,000 miles of blood vessels in Word Form : Sixty Thousand miles.
Question 13.
Which One Doesn’t Belong?
Which number does belong with the other three?
1 × 10,000 + 4 × 1,000 + 2 × 100 + 6 × 1 fourteen thousand, two hundred six
140,206
Answer:
No number is repeated, so no number belongs to other
one at tens place
4 at ones place
2 at hundredths place
and 6 at thousandths place.
Question 14.
DIG DEEPER!
Find the difference in the values of the underlined digits.
856,092 37,841
Answer:
8 is at 80 Million,
and
8 is at hundreds value
the difference is 8 X 1,00,00,000 times the other 8 value.
Use the table.
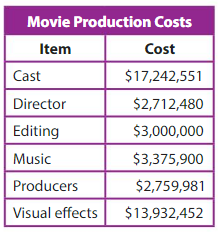
Question 15.
Modeling Real Life
Compare the values of the 3s in the music cost.
Answer: 3 is at 3 millions place and other 3 is at 3 hundreds place.
Question 16.
Modeling Real Life
Compare the values of the 2s in the cost.
Answer:
Costs Places
In cast 2 is at two hundred thousands place and 2 at thousands place.
In Director 2 is at 2 millions place and 2 at thousands place.
In Editing 2 value is not there.
In Music also 2 is not there
In Producers 2 value is at 2 millions place
In Visual effects 2 place is first at thousands place and 2 is in ones place
Question 17.
DIG DEEPER!
What is the total cost for the director and producers? Write your answer in word form.
Answer: Total cost of director-$ 2,712,480+ and cost of roducer –
$ 2,759,981 is $ 5,472,461
Word Form : five million, four hundred thousand, seventy two thousand, four hundred sixty one dollars.
Review & Refresh
Compare
Question 18.
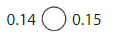
Answer:
0.14 < 0.15
0.14-0+ 1 x 1/10+4/100
0 is at ones place ,1 is at 1/10 place, and 4 is at 1 /100 place is small
0.15-0+1×1/10+5/100
0 is at ones place ,1 is at 1/10 place, and 5 is at 1 / 100 place
Question 19.
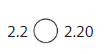
Answer:
2.2 = 2.20
2.2-2 is at ones place and .2 is at 2/10 place
2.20- 2 is at ones place ,.2 is at 2/10 place is same
Question 20.
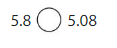
Answer:
5.8 > 5.08
5.8 – 5 is at ones place and .8 is at 1/10 place
5.08 – 5 is at ones place and .8 is at 1/100 place is small
Lesson 1.3 Patterns and Powers of 10
Explore and Grow
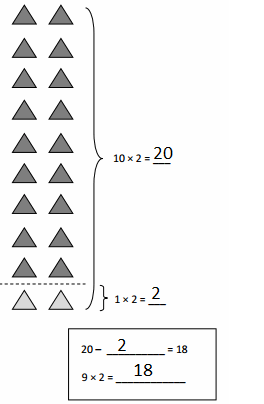
Write a multiplication expression to answer each question.
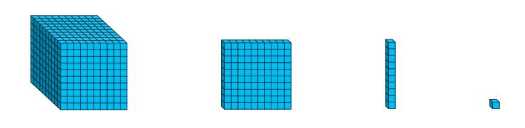
How many units are in 1 rod?
How many units are in 10 rods?
How many units are in 100 rods?
How many units are in 1,000 rods?
Answer:
In 1 rod its 1 x 100 =100
In 10 rods its 1 x 10 = 101
In 100 rods its 1 x 10 x 10 = 102
In 1,000 rods it is 1 x 10 x 10 x 10 =103
Repeated Reasoning
How many tens are in 100? in 1,000? in 10,000?
Answer: In 100 its 10 tens, in 1,000 its 100 tens and in 10,000 its 1000 tens
Think and Grow: Patterns and Powers of 10
Key Idea
A power is a product of repeated factors. The base of a power is the repeated factor. The exponent of a power gives the number of times the base is used as a factor.
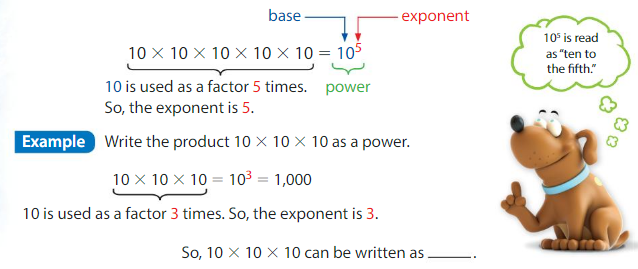
Example
Find the value of 4 × 103.

Multiply 4 by powers of 10. Look for a pattern.
4 × 101 = 4 × 10 = _40____
4 × 102 = 4 × 10 × 10 = _400_____
4 × 103 = 4 × 10 × 10 × 10 = __4,000____
So, 4 × 103 = ____4,00,000_.
Notice the pattern: In each product, the number of zeros after 4 is equal to the exponent.
Show and Grow
Question 1.
Identify the base, exponent, and power for the expression 106.
Answer:
base : 10,
exponent: 6
power :106= 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10
Question 2.
Write the product 10 × 10 × 10 × 10 as a power.
Answer:
10 x 10 x 10 x 10 as a power is 10 4
Question 3.
Find the value of 5 × 102.
Answer:
5 × 102 is
5 x 10 x 10 = 500
Apply and Grow: Practice
Find each product. Use patterns to help.
Question 4.
2 × 10 = _____
2 × 100 = _____
2 × 1,000 = _____
2 × 10,000 = ____
Answer:
2 x 10 =20
2 x 100=200
2 x 1,000= 2,000
2 x 10,000 = 20,000
Question 5.
9 × 10 = _____
9 × 100 = _____
9 × 1,000 = _____
9 × 10,000 = ____
Answer:
9 x 10 = 90
9 x 100 = 900
9 x 1,000= 9,000
9 x 10,000 = 90,000
Question 6.
5 × 10 = _____
5 × 100 = _____
5 × 1,000 = _____
5 × 10,000 = ____
Answer:
5 x 10 = 50
5 x 100= 500
5 x 1,000 = 5,000
5 x 10,000 = 50,000
Find the value of the expression.
Question 7.
104
Answer:
104= 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 10,000
Question 8.
6 × 105
Answer:
6 × 105 = 6 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 6,00,000
Question 9.
7 × 102
Answer:
7 × 102 = 7 x 10 x 10 = 700
Question 10.
5 ×10 4
Answer:
5 ×10 4= 5 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 50,000
Rewrite the number as a whole number multiplied by a power of 10.
Question 11.
20,000
Answer:
20,000=2 x 104
Question 12.
500
Answer:
500=5 X 102
Question 13.
900,000
Answer:
9,00,000=9 x 105
Number Sense
Write the number in expanded form using exponents.
Question 14.
53,124
(5 × 104) + ______
Answer:
53,214=(5 × 104) +( 3 x 103)+(1 x 102) + (2 x101)+ (4 x100)
Question 15.
8624
(8 × 102) + _______
Answer:
8624=(8 x 103 )+(6 x 102) +(2 x 101)+(4×100)
Question 16.
DIG DEEPER!
Your friend writes (3 × 104) + (5 × 103) + (2 × 102) + 4 as the expanded form of thirty-five thousand, twenty-four. Explain what your friend did wrong.
Answer:
(3 × 104) is 3 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 30,000 is Thirty Thousand
(5 × 103) is 5 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 5,000 is five thousand
(2 × 102) is 2 x 10 x 10 = 200 is two hundred not twenty
and 4 is four,
it is thirty-five thousand, two hundred and four= 35,204
not thirty-five thousand, twenty-four ≠ 35,024
35,204 is right
35,024 is wrong
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
Newton and Descartes are running for mayor. How many people voted in the election?
Find the number of votes for each candidate.
Newton: 105 = ______
Descartes: 9 × 104 = ______
Add the votes for Newton and Descartes.

______ people voted in the election.
Newton: 105 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 is 1,00,000
Descartes: 9 × 104 = 9 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 is 90,000
so total people voted is 1,00,00 + 90,000 = 1,90,000
| 1,00,000 |
| + 90,000 |
| =1,90,000 |
1,90,000 Voted in the election.
Show and Grow
Question 17.
A surf shop has been in business for two years. What are the total sales for Year 1 and Year 2 combined?
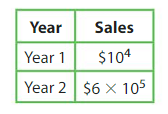
Answer:
Year 1 $ 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 =10,000
Year 2 $ 6 x 105= 6 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 6,00,000
| 10,000 |
| + 6,00,000 |
| = 6,10,000 |
there fore total sales for Year 1 and Year 2 combined is is 6,10,000 .
Question 18.
Which migration is farther? About how much farther is it?

Answer:
Chinook Salmon about 4 x 103km
4 X 10 x 10 x 10 = 4000 km
and
Leatherback Turtle about 2 X 104 km
2 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 20,000 km
So Leatherback Turtle is farther and
20,000 km – 4000 km = 16,000 km
it is 16,000 km farther
Question 9.
DIG DEEPER!
A human has about 104 taste buds. A cow has about 3 times as many taste buds as a human. About how many taste buds does a cow have? Write your answer as a whole number multiplied by a power of 10.
Answer:
(104) 3 time means (104)3
as per the law powers are multiplied 4 x 3
(104×3) = (1012)
(104×3)= 1 X (104) x (104) x (104)
(1012)= 1 x (10 x 10 x 10 x 10 ) x (10 x 10 x 10 x 10 ) x (10 x 10 x 10 x 10)
Patterns and Powers of 10 Homework & Practice 1.3
Question 1.
Identify the base, exponent, and power for the expression 103.
Answer:
base: 10
exponent: 3
power : 103= 10 x 10 x 10
Question 2.
Write 10 × 10 × 10 × 10 a power.
Answer:
10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 104
Find each product. Use patterns to help.
Question 3.
6 × 10 = ______
6 × 100 = _____
6 × 1,000 = _____
6 × 10,000 = _____
Answer:
6 x 10=6 × 101 = 60
6 x 100 =6 × 102 = 600
6 X 1,000=6 × 103 = 6,000
6 x 10,000 = 6 × 104= 60,000
Question 4.
8 × 10 = ______
8 × 100 = _____
8 × 1,000 = _____
8 × 10,000 = _____
Answer:
8 x 10=8 × 101 = 80
8 x 100 =8 × 102 = 800
8 X 1,000=8 × 103 = 8,000
8 x 10,000 = 8 × 104= 80,000
Question 5.
4 × 10 = ______
4 × 100 = _____
4 × 1,000 = _____
4 × 10,000 = _____
Answer:
4 x 10=4 × 101 = 40
4 x 100 =4 × 102 = 400
4 X 1,000= 4× 103 = 4,000
4 x 10,000 = 4 × 104= 40,000
Find the value of the expression.
Question 6.
103
Answer:
103 = 10 x 10 x 10 = 1,000
Question 7.
2 × 104
Answer:
2 × 104 = 2 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 20,000
Question 8.
9 × 105
Answer:
9 × 105 = 9 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 9,00,000
Question 9.
3 × 102
Answer:
3 × 102 = 3 x 10 x 10 = 300
Rewrite the number as a whole number multiplied by a power of 10.
Question 10.
100,000
Answer:
100,000 = 1 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 1 × 105
Question 11.
70
Answer:
70 = 7 x 10 = 7 x 101
Question 12.
6,000
Answer:
6,000 = 6 x 10 x 10 x 10 = 6 x 103
Number Sense
Write the number in standard form.
Question 13.
(3 × 102) + (8 × 101)
Answer:
(3 × 102) + (8 × 101) = 3 x 10 x 10 + 8 x 10
3 x 100 + 80
300+ 80 = 380
Question 14.
(2 × 103) + (5 × 102) + (4 × 101)
Answer:
(2 × 103) + (5 × 102) + (4 × 101) = 2 x 10 x 10 x 10 + 5 x 10 x 10 + 4 x 10
2,000 + 500 + 40
2,540
Question 15.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Newton 6 says 106 = 10 × 6. Is he correct? Explain
Answer:
No he is wrong because 106 ≠ 10 × 6 it is 10 is to be multiplied by 6 times ,
106 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10=10,00,000 is correct
Question 16.
Which One Doesn’t Belong?
Which one does not belong with the other three?
Answer:
Both are different blocks , in first block it is square and next it is cube.
Question 17.
Modeling Real Life
Each student at an elementary school votes once on this year’s field trip. How many students voted in all?
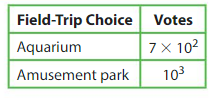
Answer:
Aquarium = 7 x 102 = 7 x 10 x 10 = 700
Amusement Park = 103 = 10 x 10 x 10 = 1000
700 + 1000 = 1,700
So total number of students voted are = 1,700.
Question 18.
Modeling Real Life
On which day did more people attend the event? How many more people?
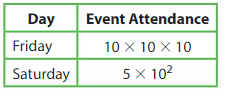
Answer:
Friday = 10 x 10 x 10 = 1,000
Saturday = 5 x 102 = 5 x 10 x 10 = 500
on Friday more people attend the event
and more are 1,000 – 500 = 500 , s0 500 more people attended.
Review & Refresh
Divide. Then check your answer
Question 19.
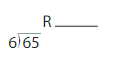
Answer:
Step 1) Start by dividing 65 by 6 to get the decimal answer as illustrated below. Note that we round the answer if necessary, but don’t worry, the final answer will still be exact.
65 / 6 = 10.83
Step 2) Next we take the Whole part of the answer in Step 1 and multiply it by the Divisor. As you can see, it does not matter if we rounded in the previous step because the Decimal part is ignored. Furthermore, the Divisor in 65 divided by 6 is 6. Thus, the Whole multiplied by the Divisor is:
10 x 6 = 60
Step 3) Finally, we will subtract the answer in Step 2 from the Dividend to get the answer. The Dividend in 65 divided by 6 is 65. Thus, our final calculation to get the answer is:
65 – 60 = 5
the answer is 5.
Question 20.
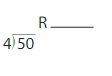
Answer:
Step 1) Start by dividing 50 by 4 to get the decimal answer as illustrated below. Note that we round the answer if necessary, but don’t worry, the final answer will still be exact.
50 / 4 = 12.50
Step 2) Next we take the Whole part of the answer in Step 1 and multiply it by the Divisor. As you can see, it does not matter if we rounded in the previous step because the Decimal part is ignored. Furthermore, the Divisor in 50 divided by 4 is 4. Thus, the Whole multiplied by the Divisor is:
12 x 4 = 48
Step 3) Finally, we will subtract the answer in Step 2 from the Dividend to get the answer. The Dividend in 50 divided by 4 is 50. Thus, our final calculation to get the answer is:
50 – 48 = 2
the answer is 2.
Question 21.

Answer:
Step 1) Start by dividing 45 by 3 to get the decimal answer as illustrated below. Note that we round the answer if necessary, but don’t worry, the final answer will still be exact.
45 / 3 = 15
the answer is 0.
Lesson 1.4 Decimals to Thousandths
Explore and Grow
Divide the square into10 equal parts. Shade one part. What part of the whole is shaded?
Fraction: Decimal:
Divide each of the 10 parts into 10 equal parts. Shade one part using a different color. What part of the whole is shaded with the second color?
Fraction: Decimal:
If you divide each of the 100 equal parts into10 equal parts, how many parts will the model have?
If you shade one of those parts, what part of the whole is shaded?
Fraction: Decimal:
Answer:
the model will have 10 parts , only 1/ 10th part is shaded, 0.1
Structure
Compare the number of hundredths to the number of tenths. Compare the number of hundredths to the number of thousandths. What do you notice?
Answer:
number of hundredths to the number of tenths is 10 to 100 , 10/100=1/10 = 0.1
number of hundredths to the number of thousandths is
100 to 1000, 100/1000 =1/10= 0.1
both has equal values 1/10 = 0.1
the number of hundredths to the number of tenths is equal to the number of hundredths to the number of thousandths
Think and Grow: Thousandths
Key Idea
In a decimal, the third place to the right of the decimal point is the thousandths place. You can write thousandths as fractions or decimals.
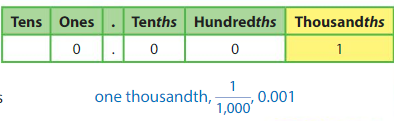
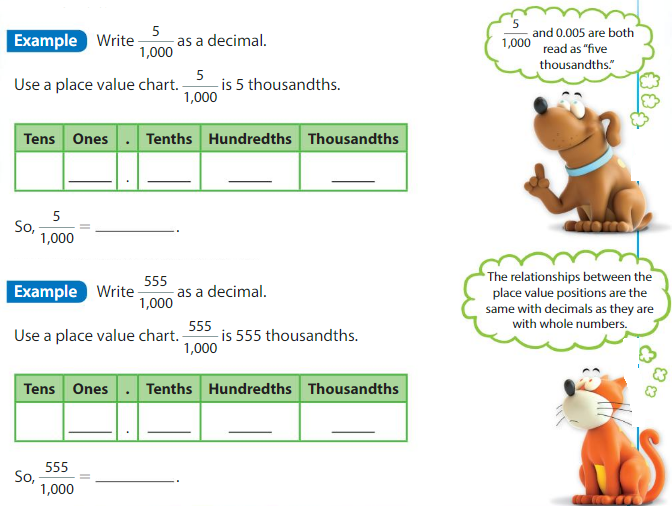
Show and Grow
Write the decimal as a fraction.
Question 1.
0.009
Answer:
0.009= 9 / 1,000 = 9 x 1/1,000
Question 2.
0.063
Answer:
0.063 = 63 / 1,000= 63 x 1/1,000
Question 3.
0.194
Answer:
0.194 = 194 / 1,000= 194 x 1/1,000
Write the fraction as a decimal
Question 4.
\(\frac{3}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{1,000}\)= 3 x 1/ 1,000= 0.003
Question 5.
\(\frac{91}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{91}{1,000}\)= 91 x 1/ 1,000 = 0.091
Question 6.
\(\frac{607}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{607}{1,000}\)= 607 x 1/1,000= 0.607
Apply and Grow: Practice
Write the decimal as a fraction.
Question 7.
0.645
Answer:
0.645= 645x 1/1,000= 645/1,000
Question 8.
0.002
Answer:
0.002=2 x 1/1,000= 2/1,000
Question 9.
0.98
Answer:
0.98= 98 x 1/ 1,000= 98/1,000
Question 10.
0.6
Answer:
0.6 = 6 x 1/10= 0.6/10
Write the fraction as a decimal.
Question 11.
\(\frac{884}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{884}{1,000}\)= 884x 1/1,000= 0.884
Question 12.
\(\frac{8}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{8}{1,000}\)= 8 x 1/1,000= 0.008
Question 13.
\(\frac{39}{100}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{39}{100}\)= 39 x 1/ 100= 0.39
Question 14.
\(\frac{1}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{10}\)= 1 x 1/10 = 0.1
Question 15.
0.4 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{10}\) is 0.4
Question 16.
0.52 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer:
0.52 is 10 times as great as 0.052
Question 17.
You use 47 of the cotton balls for an art project. What portion of the bag of cotton balls do you use? Write your answer as a decimal.

Answer:
47/100= 47 x 1/100= 0.47
Question 18.
Which One Doesn’t Belong?
Which number does not belong with the other three?
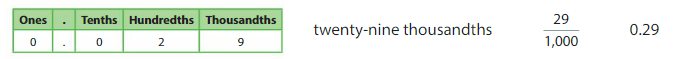
Answer:
0.29 does not belongs to other three
Question 19.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says the value of the 7 in the hundredths place of 0.877 is 10 times as great as the 7 in the thousandths place. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer:
Yes , because the value of 7 in the hundredths place as compared is 10 times as great as the 7 in the thousands place.
Question 20.
Write each fraction as a decimal. What do you notice?
\(\frac{4}{10}\), \(\frac{40}{100}\) and \(\frac{400}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{10}\)=0.4
\(\frac{40}{100}\) =0.4
\(\frac{400}{1,000}\)=0.4
number of tenths, tenths number of hundredths and hundredths number of thousandths are same.
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You put together 156 pieces of the puzzle before lunch and 148 pieces of the puzzle after lunch. What portion of the puzzle did you put together? Write your answer as a decimal.

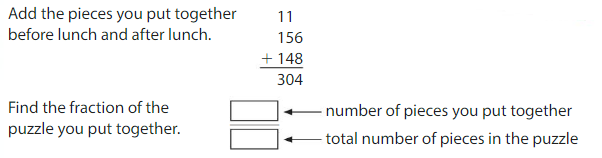
Write the fraction as a decimal.
You put together ____0.304__ of the puzzle.
Show and Grow
Question 21.
You make flash cards out of index cards. You use 50 index cards for social studies and 25 index cards for science. What portion of the pack of index cards do you use? Write your answer as a decimal.

Answer:
50 for social studies, 25 for science total is 50 + 25 = 75, total number of flash cards is 1,000 ,
75 / 1,000 or 75 by 1,000 or 75 x 1/1,000= 0.075
Question 22.
There are 458 knock-knock jokes in the book. not What fraction of the jokes in the book are knock-knock jokes?

Answer:
458/1,000 or 458 x 1/1,000 of jokes books in knock- knock jokes.
Question 23.
DIG DEEPER!
A newly hatched caterpillar was 0.02 inches long. After 2 weeks, the caterpillar grew 10 times as long as its length when it hatched. After another 2 weeks, the caterpillar grew 10 times as long as its length after 2 weeks. How long is the caterpillar now?
Answer: First week it is 0.02 inches,
in two weeks -2 weeks-0.02 x 10 = 0.2 inches
again after 2 weeks -0.2 x 10 = 2 inches
Decimals to Thousandths Homework & Practice 1.4
Write the decimal as a fraction.
Question 1.
0.735
Answer:
0.735= 735 / 1,000= 735 x 1/1,000
Question 2.
0.051
Answer:
0.051= 51 / 1,000= 51 x 1/1,000
Question 3.
0.804
Answer:
0.804 = 804 / 1,000= 804 x 1/ 1,000
Question 4.
0.2
Answer:
0.2 = 2 / 10= 2 x 1/10
Write the fraction as a decimal.
Question 5.
\(\frac{98}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{98}{1,000}\)=98 x 1/1,000= 0.098
Question 6.
\(\frac{67}{100}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{67}{100}\)= 67 x 1/100=0.67
Question 7.
\(\frac{4}{100}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{100}\)= 4 x 1/100=0.04
Question 8.
\(\frac{9}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{9}{10}\)= 9 x 1/10= 0.9
Question 9.
0.08 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer:
0.008
if 0.008 is multiplied by 10 times it becomes 0.08
Question 10.
0.001 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:
0.0001
if 0.0001 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) equals to 0.001
Question 11.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says that \(\frac{16}{1,000}\) can be written as 0.16. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: No, because if 16 / 1,000 or 16 x 1/1,000 is 0.016 not 0.16,
0.016 ≠ 0.16
so he is incorrect.
Question 12.
Precision
Thirteen unit cubes are taken from the thousand cube. Write a fraction and a decimal to represent how many unit cubes are left.
Answer:
13 units cubes are taken
Total number of units are 1000
left are from 1,000-13/1,000=87/1000
87 / 1,000 and 0.087 cubes are left
Question 13.
DIG DEEPER!
Write the number represented by each point on the number line.
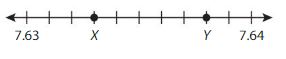
Point X: _____
Point Y: ___
Answer:
on the number line Point X = 7.633 as we move from 7.63 to three places forward
so Point X is 7.633
on the number line Point Y = 7.638 as we move from 7.63 its eighth place forward
and Point Y is 7.638
Question 14.
Modeling Real Life
A restaurant owner has a 1,000-count box of napkins. She puts 125 of the napkins on tables. What portion of the box of napkins does she use for the tables? Write your answer as a decimal.
Answer:
Restaurant has 1,000 count box of napkins and keeps 125 on table so portion of the box she uses is 125/1,000= 125 x 1/ 1,000= 0.125
Question 15.
DIG DEEPER!
Your friend has a recipe book with 1,000 recipes. She wants to try two new recipes each week. What fraction of the recipes in the book will she have tried after 1 year?
Answer:
In a year there are almost 52 weeks. Each week 2 means 2 x 52 =approximately 104 recipes in a year.
so in a year she would have tired 104 / 1,000= 104 x 1/1,000 = 0.104 recipes.
Review & Refresh
Question 16.
Extend the pattern of shapes by repeating the rule “square, octagon, pentagon, octagon ”What is the 48th shape in the pattern?

Answer:
” square, octagon, pentagon, octagon, hexagon, octagon , heptagon , octagon,
octagon, octagon, nonagon, octagon , decagon, octagon,
Lesson 1.5 Place Value with Decimals
Explore and Grow
Model the number. Draw your model.
Then write the value of each digit.
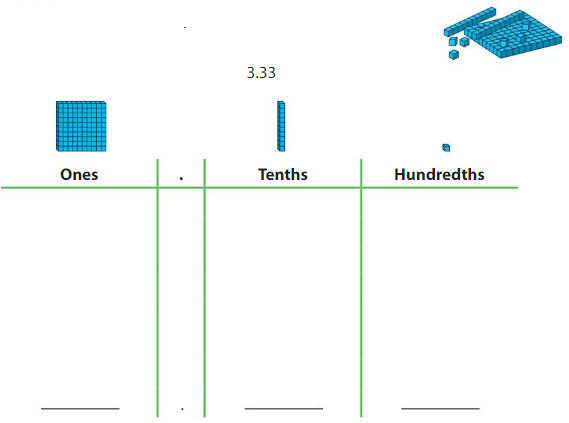
Answer:
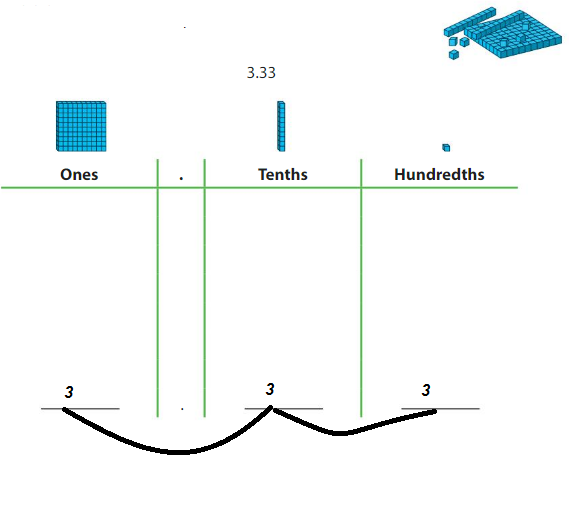
from the model 3.33 =
0nes digit is – 3
tenths digit is 3/10 =0.3
hundredths digit is 3/ 100 = 0.03
Repeated Reasoning
Compare the value of the ones digit to the value of the tenths digit. Then do the same with the tenths and the hundredths digits. Explain why you can use base ten blocks to model ones, tenths, and hundredths.
Answer:
a digit in one place represents one and 10 times more what it represents in the place to its right and that is tenths digit.
Similarly a digit in tenths place represents tenth and 10 times more what it represents in the place to its right and that is hundredths digit.
Each place to the left is 10 times the size of the place to the right, and base 10 blocks are the best way to model ones, tenths, and hundredths.

Think and Grow: Place Value with Decimals
Key Idea
In a place value chart, whole numbers are to the left of the decimal point. Decimals are to the right of the decimal point.
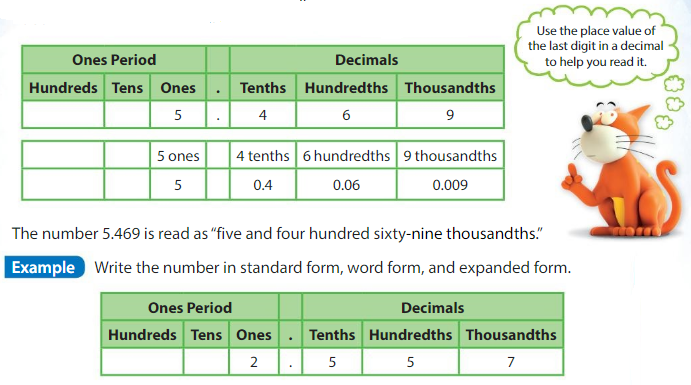
Standard form:2.557
Word form:” Two and five hundred fifty-seven thousandths”
Expanded form: 2 × 1 + __5__ ×\(\frac{1}{10}\)____ + 5 × \(\frac{1}{100}\) + _7_ × \(\frac{1}{1000}\)__
Show and Grow
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 1.
Standard form: 0.398
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: “Three hundred ninety – eight thousandths”
Expanded form: 3 x (1/10) + 9 x (1/100) + 8 x (1/1,000)
Question 2.
Standard form:
Word form: eight and forty-six thousandths
Expanded form:
Answer:
Standard form:8.046
Expanded form: 8 x 1 + (4 /100) + (6 / 1,000)
Question 3.
Compare the values of the 5s in the number 2.557.
Answer: at first 5s place value is at tenths and next its place value is at hundredths .
Apply and Grow: Practice
Write the value of the underlined digit.
Question 4.
0.418
Answer:
4 is at tenths value place
Question 5.
5.296
Answer:
9 is at hundredths value place
Question 6.
3.806
Answer:
8 is at tenths value place
6 is at thousandths value place
Question 7.
0.547
Answer:
7 is at thousandths value place
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 8.
Standard form:
Word form:
Expanded form: 4 × 1 + 9 × \(\frac{1}{10}\) + 8 × \(\frac{1}{1,000}\)
Answer:
Standard form: 4.908
Word form:” Four and nine hundredth – eight thousandths”
Question 9.
Standard form: 0.125
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: “one hundred twenty – five thousandths”
Expanded form: 1 x (1/10) + 2 x (1 /100) +5 x (1 / 1,000)
Question 10.
Compare the values of the 4s in the number 0.844.
Answer:
at first 4s place value is at hundredths and next 4s place value is at thousandths
Question 11.
Compare the values of the 3s in the number 3.367.
Answer: at first 3s place value is at ones place and next 3s place value is at tenths place
Question 12.
A pygmy jerboa weighs one hundred thirty-two thousandths pound. Write this number in standard form.

Answer:
The Standard Form of pygmy jerboa’s -one hundred thirty-two thousandths pound weighs is 0.132 pound
Question 13.
Reasoning
Is 9.540 equivalent to 9.54? Explain.
Answer:
Yes. 9.540 is equivalent to 9.54 because at thousandths value its 0, so zero multiplied by any number is zero.
Therefore both are equivalent.
Question 14.
DIG DEEPER!
Write three decimals that are equivalent to 6 × 1 + 4 × \(\frac{1}{10}\) .
Answer:
the three equivalent decimals are of 6 .04 are 6.040, 6.0400, 6.04000
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
How do the values of the 3s in the masses of the fruits compare?
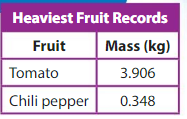
Use a place value chart to help you find the value of each 3.
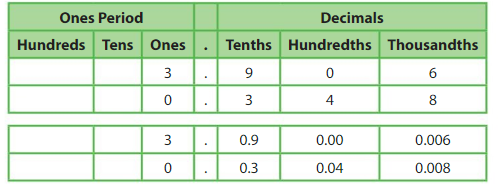
The value of the 3 in the mass of the tomato is _one_____ .
The value of the 3 in the mass of the chili pepper is __tenths___.
So, the value of the 3 in the mass of the tomato is __10_____ times the value of the 3 in the mass of the chili pepper. Also, the value of the 3 in the mass of the chili pepper is ___1/10__ the value of the 3 in the mass of the tomato.
Show and Grow
Question 15.
Two baseball players have batting averages of 0.358 and 0.345. How do the values of the 5s in the batting averages compare?
Answer:
In 0.358 the place value of 5s is at tenths place and in
0.345 the place value of 5s is at thousandths place.
Question 16.
The stopwatch shows a runner’sritethe100-meter dash time. Write the time in words.

Answer:
15.76 seconds time in words is Fifteen and seven tenths and six hundredths
Question 17.
DIG DEEPER!
You exchange 1 U.S. dollar for Australian dollars and 1 U.S. dollar for Kuwaiti dinars. Do you have 10 times as many Australian dollars as Kuwaiti dinars? Explain.

Answer:
Yes, Because 1 Australian dollars = 1.302 of 0.302 of Kuwaiti dinars,
if we multiply 0.302 by 10 it becomes 1.302 which is equal to 1 Australian dollars.
[0.302 x 10 = 1.302]
so 1 Australian dollars is 10 times more than the 1 Kuwaiti dinars.
Place Value with Decimals Homework & Practice 1.5
Write the value of the underlined digit.
Question 1.
5.437
Answer:
5 at ones place
4 at tenths place
3 at hundredths place
7 at thousandths place
Question 2.
0.852
Answer:
the underlined digit is 2 at thousandths place,
its value is 2 x 1/1000= 2/1000
Question 3.
0.962
Answer:
the underlined digit is 6 at hundredths place
its value is 6 x 1/100= 6 /100
Question 4.
4.165
the underlined digit is 1 at tenths place
its value is 1x 1/10 = 1/10
Answer:
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 5.
Standard form: 9.267
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: nine and two tenths six hundredths seven thousandths.
Expanded form : 9+ 2 x 1/10 + 6 x 1/100 + 7 x 1/1000
Question 6.
Standard form:
Word form: two and forty-three thousandths
Expanded form:
Answer:
Standard form : 0.243
Expanded form: 2 x 1/10+4 x 1/100+3 x 1/1000
Question 7.
Compare the values of the 6s in the number 1.668.
Answer:
first 6s at tenths place and next 6s at hundredths place
Question 8.
Compare the values of the 7s in the number 7.704.
Answer:
first 7s at ones place and next 7s at tenths place
Question 9.
A pygmy possum weighs 0.097 pound. Write this number in word form.

Answer:
pygmy weighs 0.097 pound and its
word form is nine hundredths and seven thousandths
Questio 10.
Which One Doesn’t Belong?
Which one does not belong with the other three?
Answer:
no number belongs to other three because 5 is at tenths place
one at hundredths place and 4 at thousandths all are at different places.
Question 11.
Reasoning
Which number cards are equal to the value of the underlined digit?

Answer:
2 x 1/1,000 , two thousandths and 0.002 are equal to the value of the underlined digit.
Question 12.
Modeling Real Life
How do the values of the 5s in the heights of the plants compare?
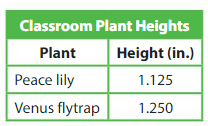
Answer:
In Peace lily the 5s place is at thousandths
and in Venus flytrap the 5s place is at hundredths
Question 13.
Modeling Real Life
The world’s largest gold nugget is located in Las Vegas, Nevada. It has a mass of about 27.247 kilograms. Write how to say the nugget’s mass in words.

Answer:
the mass of gold nugget in Las Vegas is 27.247 kilograms given
In Words form it is twenty seven and two tenths four hundredths and seven thousandths
Review & Refresh
Compare.
Question 14.
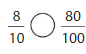
Answer:
8/10 =0.8
80/100=0.8
both are equal 8/10 = 80/100
Question 15.
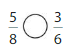
Answer:
5/8 = 0.625
3/6= 0.5
0.625 > 0.5,
5/8 > 3/ 6, 5/8 is greater than 3/6
Question 16.
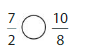
Answer:
7/2= 3.5
10/8=1.25
so 7/2 is greater than 10/8.
7/2 > 10/8
Lesson 1.6 Compare Decimals
Explore and Grow
Use models to compare the decimals.

Answer:
0.62 >0.26, 0.62 is greater than 0.26, 0.6 is greater than o.2
0.80= 0.8, 0.80 both are equal
3.5 < 3.55, 3.55 is greater than 3.50
Reasoning
How can you use a place value chart to compare two decimals? Use a place value chart to check your answers above.
Answer:
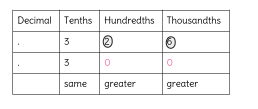
we use another table to compare with the previous and write the answer.
Think and Grow: Compare Decimals
Example
Compare 3.769 and 3.749.
Use a place value chart. Start at the left. Compare the digits in each place until the digits differ.
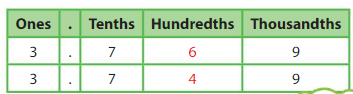
The digits in the ones place and the tenths place are the same. Compare the hundredths.

Example
Compare 2.4 and 2.405.
Use place value. Line up the decimal points. Start at the left. Compare the digits in each place until the digits differ.
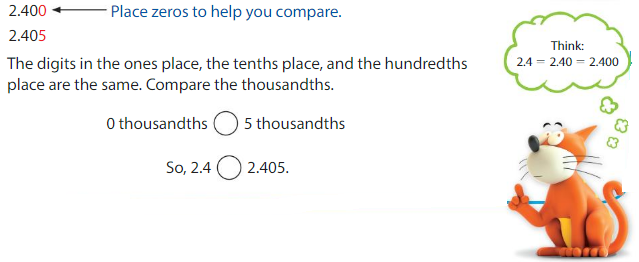
2.4<2.405
Show and Grow
Compare
Question 1.
Answer:
| Ones |
. |
Tenths |
Hundredths |
Thousandths |
| 9 |
. |
0 |
6 |
3 |
| 9 |
. |
0 |
6 |
7 |
| Same |
. |
Same |
Same |
Greater |
So 9.063 < 9.067
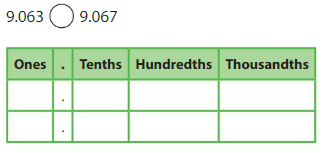
Question 2.
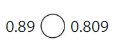
Answer:
| Ones |
. |
Tenths |
Hundredths |
Thousandths |
| 0 |
. |
8 |
9 |
0 |
| 0 |
. |
8 |
0 |
9 |
| Same |
. |
Same |
Greater |
Greater |
So 0.89 > 0.809,
Apply and Grow: Practice
Compare.
Question 3.
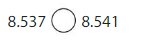
Answer:
| Ones |
. |
Tenths |
Hundredths |
Thousandths |
| 8 |
. |
5 |
3 |
7 |
| 8 |
. |
5 |
4 |
1 |
| Same |
. |
Same |
Greater |
Greater |
8.537 < 8.541
Question 4.
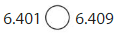
Answer:
6.401 < 6.409, since 0.009 is greater than 0.001
Question 5.
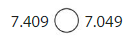
Answer:
7.409 > 7.049 since 7.4 is greater than 7.0
Question 6.
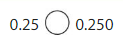
Answer:
0.25 = 0.250
Both are equal
Question 7.

Answer:
2.701 >2.700, since 0.001 is greater than 0.000
Question 8.
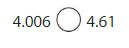
Answer:
4.006 < 4.61, since 4.6 is greater than 4.0
Question 9.

Answer:
0.041 < 41.6, 41 is greater than 0
Question 10.

Answer:
0.007 < 0.7 as 0.7 is greater than 0.007
Order the decimals from least to greatest.
Question 11.
321.499, 325.499, 321.489
Answer:
321.499, 325.499, 321.489 from least to greatest
as 321.489 is smaller than 321.499 and 321.499 is smaller than 325.499
so 321.489 , 321.499 , 325.499
Question 12.
9.7, 9.64, 9.78
Answer:
9.7, 9.64, 9.78 from least to greatest
9.64 is smaller than 9.7 and 9.7 is smaller than 9.78
so 9.64, 9.7 , 9.78
Open-Ended
Complete the number to make the statement true.
Question 13.

Answer:
10.321 > 10.311
as 10.311 is smaller than 10.321
Question 16.
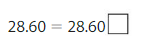
Answer:
28.60 = 28.600
Both are equal
Question 15.
Number Sense
Is 0.472 greater than or less than \(\frac{47}{1,000}\)? Explain.
Answer:
0.472, 0.047
0.475 is greater than 0.047,
as 4 in the tenths place is greater than 0 in the others tenth place
Question 16.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says that 45.6 is less than 45.57 because 6 is less than 57. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer:
Friend says 45.6 is less than 45.57
No ,he is wrong as the 6th in tenths place is greater than 5, in the tenths place
so he is wrong 45.60 > 45.57 not less
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You, your friend, and your cousin compete at a gymnastics competition. Your floor routine score is 15.633. Your friend’s score is 15.533, and your cousin’s score is 15.635. Order the scores from least to greatest.

Use a place value chart. Compare the digits in each place until the digits differ.
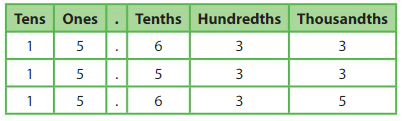
_15.533______ is the least
Write the remaining numbers in the place value chart. Compare the digits in each place until the digits differ.
15.633 ,15.635
as 15.533 is less than 15.633 as 5 at tenths place is less than 6 at tenths place
and 15.633 is less than 15.653 as 3 at hundredths place is less than 5 at hundredths place
So, the scores from least to greatest are 15.533, 15.633 and 15.635
Show and Grow
Question 17.
You stand on one leg for 2.75 minutes, your friend stands on one leg for 2 minutes, and your cousin stands on one leg for 2.25 minutes. Order the amounts of time from least to greatest.
Answer:
You – 2.75 min , Friend – 2.00 min and cousin for 2.25 min
2.00< 2.25 ,2.00 is less than 2.25 as 0 at tenths place is less than 2 at tenths place
2.25 < 2.75, 2.25 is less than 2.75 as 2 at tenths place is less than 7 at tenths place
so From Least to Greatest : 2.00 min, 2.25 min, 2.75 min
Question 18.
DIG DEEPER!
You, Newton, Descartes, and your friend each have a tablet. The table shows the screen display sizes. Your friend’s tablet has the greatest display size. Your tablet’s display size is greater than Newton’s but less than Descartes’s. What is the display size of your tablet.
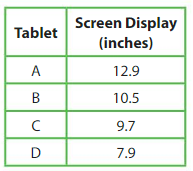
Answer:
Y-Your, N-Newton’s ,F-Friend- 12.9, D-Descartes
Given Friend has greatest display size F= 12.9
Y – N ,given Your tablet’s display size is greater than Newton’s, N< Y and yours is less than Descartes’s Y < D
therefore N < Y <D < F, Newton’s< Yours<Descartes’s<Friend
so N-Newton’s- 7.9, Y-Your-9.7,D-Descartes-10.5,F-Friend-12.9
Compare Decimals Homework & Practice 1.6
Write which place to use when comparing the numbers.
Question 1.
0.521
0.576
Answer:
2 at hundredths place is smaller than 7 at hundredths place
so 0.521 < 0.576
Question 2.
17.422
17.946
Answer:
4 at tenths place is small than 9 at tenths place
so 17.422 < 17.946
Question 3.
9.678
9.67
Answer:
8 at thousandths place is greater than 0 at thousandths place
9.678 > 9.670
Compare.
Question 4.
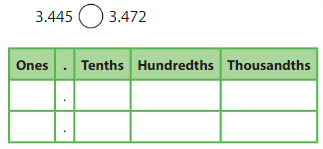
Answer:
4 at hundredths place is smaller than 7 at hundredths place
so 3.445 is smaller than 3.472
3.445 < 3.472
Question 5.
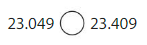
Answer:
0 at tenths place is smaller than 4 at tenths place
so 23.049 < 23.409
Question 6.

Answer:
4 at tenths place is greater than 3 at tenths place
75.4 > 75.391
Question 7.
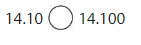
Answer:
All given place values are same
so 14.100 or 14.10 = 14.100
Question 8.

Answer:
the value of 5s at hundredths place is more than 0 in other hundredths place
4.05> 4.005
Question 9.

Answer:
15.2, 15.002
2 at tenths place is greater than 0 at tenths place
15.2 > 15.002
Question 10.
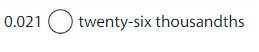
Answer:
0.021, 0.026
1 at thousandths is smaller than 6 at thousandths place
0.021 < 0.026
Order the decimals from least to greatest.
Question 11.
2.75, 0.2, 0.275
Answer:
0.2 < 0.275 as 0 at hundredths place is less than 7 at hundredths place
0.275<2.75 as 0 at ones place is less than 2 at at ones place
so from least to greatest 0.2, 0.275, 2.75
Question 12.
56.01, 56.1, 56.001
Answer:
56.001 < 56.01 as 0 at hundredths place is less than 1 at hundredths place
56.01 < 56.1 as o at tenths place is less than 1 at tenths place
56.001 , 56.01, 56.1
Open-Ended
Complete the number to make the statement true.
Question 13.
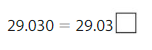
Answer:
29.030 = 29.030
both the place values are same
Question 14.
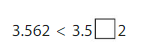
Answer:
3.562 <3.562
as the value of 6 is at hundredths place so the other value at hundredths place is 6.
Question 15.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Newton says 8.51 is less than 8.492 because 8.51 has fewer digits after the decimal point than 8.492. Is he correct? Explain.
Answer:
No, he is not correct its not the digits after the decimal point is fewer
but the 5s at tenths place is greater than 4 at the tenths place so
8.51 is greater than 8.492, 8.51 > 8.492
Question 16.
Open-Ended
Descartes is thinking of a number less than 46.922 and greater than 46.915. What could Descartes’s number be?
Answer:
The numbers can be 46.916, 4 6.917, 46.918, 46.919, 46.920 or 46.921 and
all these numbers are less than 46.922 and greater than 46.915.
Question 17.
Modeling Real Life
Player A’s batting average is 0.300, Player B’s batting average is 0.333, and Player C’s batting average is 0.313. Order the batting averages from greatest to least.
Answer:
B- 0.333, C-0.313 , A – 0.300
0.333 is great than 0.313 as 3 at hundredths place is great than 1 at hundredths place
so 0.333>0.313
0.313 is greater than 0.300 as 1 at hundredths place is great than 0 at hundredths place
0.313 > 0.300
the batting averages from greatest to least are B> C> A=0.333 > 0.313 >0.300
batting averages from greatest to least 0.333,0.313,0.300
Question 18.
Modeling Real Life
A gasoline station customer pumps more than 9.487 gallons of gasoline but less than 10 gallons. Which display could be his?

Answer:
Given A gasoline station customer pumps more than 9.487 gallons but less than 10 gallons
as 9.003 is less than 9.487 so not 9.003
as 9.499 is greater than 9.487 and even less than 10.000 so it is 9.499
as 9.406 is less than 9.487 so it cannot be 9.406
as 9.872 is greater than 9.487 and even less than 10.000 so it can be 9.872
so the displays can be 9.499 or 9.82
as both are more than 9.487 gallons and less than 10 gallons
Review & Refresh
Round the number to the place of the underlined digit.
Question 19.
7,851
Answer:
the round place of 5 is 7,850
Question 20.
9,462
Answer:
the round place of 9 means 10,000 or 9,500
Question 21.
4,983
Answer:
the round place of 9 – 5,000
Question 22.
51,504
Answer:
the round place of 1- 52,504
Lesson 1.7 Round Decimals
Explore and Grow
Plot the numbers on the number line. Which numbers round to 3? Which numbers round to4? How do you know?
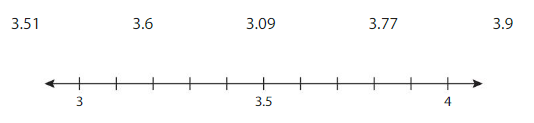
Answer:
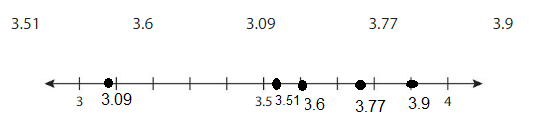
3, 3.09, 3.5, 3.51, 3.6, 3.77, 3.9 , 4
The numbers round to 3 are 3.09
The numbers round to 4 are 3.51, 3.6, 3.77 , 3.9
Repeated Reasoning
Show how you can use a number line to round 3.09, 3.51, and 3.77 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
3.09 to the nearest tenth is 3.10
3.51 to the nearest tenth is 3.50
3.77 to the nearest tenth is 3.80
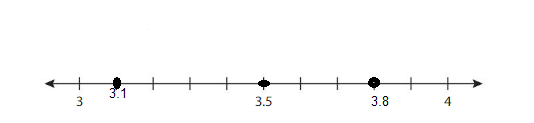
Think and Grow: Round Decimal Number
Example
Use a number line to round 7.36 to the nearest tenth.
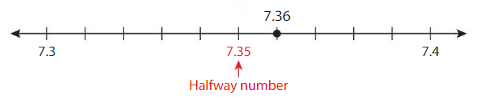
7.36 is closer to 7.4 than it is to 7.3.
So, 7.36 rounded to the nearest tenth is __7.40____.
Example
Use place value to round 2.185 to the nearest whole number and to the nearest hundredth.
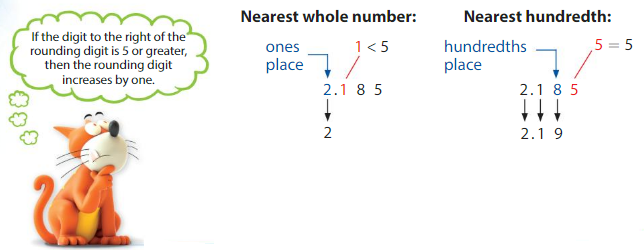
So, 2.185 rounded to the nearest whole number is __2.2_____.
2.185 rounded to the nearest hundredth is ___2.200___.
Show and Grow
Round the number to the place of the underlined digit.
Question 1.
12.67
Answer:
the round place of digit 6 is 12.70
Question 2.
0.439
Answer:
the round place of digit 4 is 0.5
the round place of digit 3 is 0.44
the round place of digit 9 is 0.440
Question 3.
2.555
Answer:
the round place of digit 2 is 3.000
Question 4.
5.409
the round place of digit 4 is 5.400
Question 5.
Round 0.68 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
0.68 to the nearest tenth is 0.70, 6 at tenths place becomes 7
Question 6.
Round 1.715 to the nearest hundredth.
Answer:
1.715 to the nearest hundredth is 1.720, 1 at hundredths place becomes 2
Question 7.
Round 4.07 to the nearest whole number.
Answer:
4.07 to the nearest whole number becomes 4.00 or 4
Question 8.
Round 0.289 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
0.289 to the nearest tenth is 0.300 as 2 becomes 3 at tenths place.
Apply and Grow: Practice
Round the number to the place of the underlined digit.
Question 9.
1.482
Answer:
the underlined digit is 8 ,so its value becomes 1.490
Question 10.
5.093
Answer:
the underlined digit is 0 so its value becomes 5.100
Question 11.
8.502
Answer:
the underlined digit is 8 so its value becomes 9.000
Question 12.
34.748
Answer:
if it is underlined at 3 it becomes 35.000
if it is underlined at 4 it becomes 35.000
if it is underlined at 7 it becomes 35.000
if it is underlined at 4 it becomes 34.800
if it is underlined at 8 it becomes 34.750
Question 13.
Round 2.619 to the nearest whole number.
Answer:
the value of 2.619 becomes 3.000
Question 14.
Round 7.825 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
the value of 7.825 to the nearest tenth is 7.900
Question 15.
Round 92.701 to the nearest ten.
Answer:
the value of 92.701 to the nearest ten 93.000
Question 16.
Round 4.263 to the nearest hundredth.
Answer:
the value of 4.263 to the nearest hundredth is 4.270
Question 17.
Round 0.829.
Nearest whole number:
Nearest tenth:
Nearest hundredth:
Answer:
Round 0.829
Nearest whole number:0.900
Nearest tenth:0.830
Nearest hundredth:0.830
Question 18.
Round 18.062.
Nearest whole number:18.100
Nearest tenth:18.070
Nearest hundredth:18.063
Answer:
Question 19.
A baby harp seal weighs 25.482 pounds. Round this weight to the nearest tenth of a pound.

Answer:
Given a baby harp seal weighs 25.482 pounds and the nearest tenth is 25.000 pounds
So the weight of baby harp seal is 25.000 pounds.
Name the place value to which the number was rounded.
Question 20.
8.942 to 8.94
Answer:
It was rounded at hundredths value place
Question 21.
0.164 to 0.2
Answer:
It was rounded at tenths value place
Question 22.
15.826 to 16
Answer:
It was rounded at whole value place
Question 23.
Writing
Explain what happens when you round 2.999 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
2.999 round value becomes 3.000 as all value places at tenths, hundredths, thousandths are 9 it becomes increased as we move so it ones value increases by 1 and becomes round 3.000.
Question 24.
DIG DEEPER!
To what place should you round 23.459 to get the greatest number? the least number? Explain.
Answer:
To make 23.459 to greatest number the value of 4s at tenths becomes 5,
23.500 and to make 23.500 round make 5 at tenths value increased and make ones value 3 as 4 so we get 24.000
and to make 23.459 to least number the value at hundredths 5 becomes 0 ,
23.400 and to make 23.400 round make 4 at tenths value as decreased to 0 and ones value same as 3 it becomes as 23.000
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
Gasoline prices are listed to the nearest thousandth of a dollar. The final price is rounded to the nearest hundredth. About how much does a customer pay for 1 gallon of regular gasoline at the station shown?

Think: What do you know? What do you need to find? How will you solve?
Use place value to round the price of 1 gallon of regular gasoline, $2.799, to the nearest hundredth.
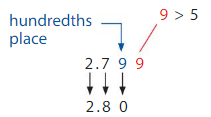
So, a customer will pay about $ ___$ 2.800____ for 1 gallon of gasoline.
Show and Grow
Use the table.
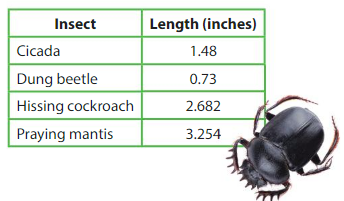
Question 25.
What is the length of the praying mantis rounded to the nearest hundredth?
Answer:
Given praying mantis as 3.254 so the nearest hundredth becomes 3.26
Praying mantis becomes 3.260
Question 26.
What is the length of the cicada rounded to the nearest tenth?
Answer:
Given cicada 1.48 so rounded to the nearest tenth becomes 1.50
Cicada becomes 1.50
Question 27.
What is the length of the hissing cockroach rounded to the nearest tenth?
Answer:
Given Hissing cockroach 2.682 so rounded to the nearest tenth is 2.700
Hissing cockroach becomes 2.700
Question 28.
DIG DEEPER!
You have about $3 in coins. Write one possible combination of coins that represents the least amount of money you could have. Write another combination of coins for the greatest amount of money you could have.
Answer:
$3 Least amount of money combinations – 1. $ 1.0, $1.0 2.$ 1.0, $1.5
3.$0.5, $ 2.0 all combinations becomes less than $3
$ 3 greatest amount of money combinations- 1. $1.0, $ 2.5 2.$1.5 ,$2.0
3. $2.0 , $ 2.0 all combinations becomes more than $3
Round Decimals Homework & Practice 1.7
Round the number to the place of the underlined digit.
Question 1.
49.012
Answer:
the underline digit is 4 its round number 4 becomes 5 so it is 50.000
Question 2.
2.308
Answer:
the underline digit is 2 its round number 2 becomes as 2.000
Question 3.
9.647
Answer:
the underline digit is 6 its round number 6 becomes 7 so it is 9.700
Question 4.
7.519
Answer:
the underline digit is 1 its round number 1 becomes 2 so it is 7.520
Question 5.
Round 8.436 to the nearest hundredth.
Answer:
8.436 to the nearest hundredth, 3 becomes 4 so it is 8.440
Question 6.
Round 15.159 to the nearest ten.
Answer:
15.159 to the nearest ten ,1 becomes 2 so it is 15.200
Question 7.
Round 1.602 to the nearest whole number.
Answer:
1.602 to the nearest whole number is 2.0
Question 8.
Round 3.619 to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
3.619 to the nearest tenth, so 6 becomes 7 it is 3.700
Question 9.
Round 4.183.
Nearest whole number:
Nearest tenth:
Nearest hundredth:
Answer:
Round 4.183.
Nearest whole number:4.000
Nearest tenth:4.200
Nearest hundredth:4.200
Question 10.
Round 9.076.
Nearest whole number:
Nearest tenth:
Nearest hundredth:
Answer:
Round 9.076.
Nearest whole number:9.000
Nearest tenth:9.100
Nearest hundredth:9.080
Name the place value to which each number was rounded.
Question 11.
16.932 to 20
Answer:
16.932 at Tens value it is rounded so it becomes 20
Question 12.
0.581 to 0.58
Answer:
0.581 to 0.58
0.581 at Thousandths value has been rounded so 0.58
Question 13.
7.429 to 7.4
Answer:
7.429 to 7.4
7.429 at Hundredths value has been rounded so 7.4
Question 14.
Structure
Round ★ to the nearest tenth.
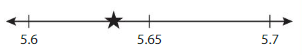
Answer:
the nearest tenth * in the number line is showing at 5.64
Question 15.
Precision
The area of a campground is exactly halfway between 25.9 acres and 26 acres. What is the area of the campground?
Answer:
Halfway of 25.9 and 26.0 is 25.90+25.60=51.50/2 = 25.75 acres
So the area of the campground is 25.75 acres.
Question 16.
Open-Ended
Name two different numbers that round to 3.8 when rounded to the nearest tenth.
Answer:
The two numbers that are round to 3.8 when rounded to the nearest tenth place the value becomes 4.0 and 3.90
Question 17.
Open-Ended
Name two different numbers that round to 7.42 when rounded to the nearest hundredth.
Answer:
The two numbers that round to 7.42 when rounded to the nearest hundredth place the value becomes 7.50 and 7.40
Use the table.
Question 18.
Modeling Real Life
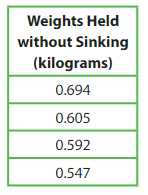
Your science class designs and tests four model boats to find out how much weight they can hold without sinking. What is the greatest weight rounded to the nearest tenth that a boat can hold?
Answer:
Given weights held without sinking in kilograms are
0.694,0.605,0.592,0.547 among all the weights the greatest weight rounded to the nearest tenth that a boat can hold is (0.694) i.e 0.7 kilograms
Question 19.
Modeling Real Life
What is the least weight rounded to the nearest hundredth that a boat can hold?
Answer:
The least weight rounded to the nearest hundredth is (0.547)- o.5 kilograms a boat can hold
Review & Refresh
Find the product.
Question 20.
7 × 40
Answer:
The product of 7 X 40 = 280
Question 21.
5,000 × 9
Answer:
The product of 5,000 x 9 = 45,000
Question 22.
8 × 200
Answer:
The product of 8 x 200=1,600
Place Value Concepts Performance Task
There are 18 species of penguins. Scientists have estimated the populations of 16 penguin species.
Question 1.
What fraction of penguin species have unknown populations?
Answer:
Given total is 18 species of penguins out of which Scientists have estimated the populations of 16 penguin species. so unknown is 18-16/18=2/18,
so 2/18=1/9 of penguin species have unknown populations
Question 2.
Several species of penguins and their estimated populations and locations are shown.

a. Are there more emperor penguins or rockhopper penguins? Explain.
b. Which species of penguin has the greatest population? Explain.
c. About how many penguins live in Antarctica? Round your answer to the nearest hundred thousand.

d. The Galápagos penguin is an endangered species. There are about 1,000 times as many macaroni penguins as Galápagos penguins. About how many Galápagos penguins are there?
Answer:
a. Rock hopper penguins are more than Emperor
2,460,000>595,000 as 2,460,000 is greater than 595,000 so Rock hopper penguins are more
B. Macaroni species 18 x 106 of penguin has the greatest population as compared to Emperor 595,000,Adelie 4,000,000+7,00,000+40,000=4,740,000 and
Rockhopper-2,460,000
among all the species Macaroni 18 x 106– species is more.
C. Macaroni + Adelie + Rockhopper +Emperor
18,000,000+4,740,000+ 2,460,000 + 595,000 = 25,795,000
25,785,000 to the nearest hundred thousand is 26,000,000
So there are almost 26,000,000 penguins live in Antarctica.
d. 1,000 times as many macaroni penguins as Galápagos penguins is
18 x 106 x 1 x 1000 = 18 x 109
So there are 18 x 109 Galápagos penguins available
Place Value Concepts Activity
Place Value Plug In
Directions:
1. Players take turns.
2. On your turn, roll six dice. Arrange the dice into a six-digit number that matches one of the descriptions.
3. Write your number on the lines.
4. The first player to fill in all of the numbers wins!
Answer:
Place Value Concepts Chapter Practice
1.1 Place Value Patterns
Use a place value chart to answer the question.
Question 1.
What number is 10 times as great as 4,000?
Answer:
10 times as great as 4,000 is 10 x 4,000= 40,000
Question 2.
What number is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 8,000?
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{10}\) of 8,000 is 8,000/10 = 800
Question 3.
10,000 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer:
10,000 is 10 times as great as 1,000
Question 4.
70 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:
70 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 700
Question 5.
Complete the table.
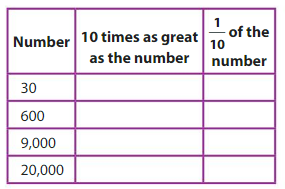
Answer:
300 is 10 times as great as 30 and 30 x 1/10 is 3
6,000 is 10 times as great as 600 and 600 x 1/10 is 60
90,000 is 10 times as great as 9,000 and 9,000 x 1/10 is 900
2,00,000 is 10 times as great as 20,000 and 20,000 x 1/10=2,000
Question 6.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says 500 is 10 times as great as 5,000. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer:
No, My friend is wrong because 500 is not 10 times great as 5,000,
500 < 5,000.
1.2 Place Value with Whole Numbers
Question 7.
Write the number in two other forms.
Standard form: 456,701
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: Four hundred fifty six thousand, seven hundred and one
Expanded form:4 x 100000 + 5 x 10000 + 6 x 1000 + 7 x 100 + 1
Question 8.
Write the number in two other forms.
Standard form:
Word form: Eight million, sixty thousand, five hundred seventy-three
Expanded form:
Answer:
Standard form:8,060,573
Expanded form:8 x 1000000+6 x 10000 + 5 x 100 + 7 x 10 + 3
Question 9.
Compare the values of the 4s in the number 900,441,358.
Answer:
4s value is at lakh or hundred thousandths place and another 4s place is at ten thousandths place.
Question 10.
Write the values of the 6s in the number 96,672.
Answer:
The values of the 6s in the number 96,672 are
6s place is at thousand and another 6s is at hundreds place
Compare.
Question 11.
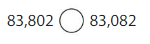
Answer:
83,802 > 83,082
The value at hundred 8 is more/great to 0 at hundreds place
Question 12.

Answer:
2,498,576 > 2,477,583
The value at 9 at ten thousands place is more/great than 7 at ten thousands place
1.3 Patterns and Powers of 10
Question 13.
Write 10 × 10 as a power.
Answer:
10 × 10 as a power is 102
Find each product. Use patterns to help.
Question 14.
4 × 10 = _____
4 × 100 = ______
4 × 1,000 = _____
4 × 10,000 = ______
Answer:
4 × 10 = 40
4 × 100 = 400
4 × 1,000 = 4,000
4 × 10,000 =40,000
Question 15.
3 × 10 = _____
3 × 100 = ______
3 × 1,000 = _____
3 × 10,000 = ______
Answer:
3 × 10 = 30
3 × 100 = 300
3 × 1,000 = 3,000
3 × 10,000 = 30,000
Question 16.
7 × 10 = _____
7 × 100 = ______
7 × 1,000 = _____
7 × 10,000 = ______
Answer:
7 × 10 = 70
7 × 100 = 700
7 × 1,000 = 7,000
7 × 10,000 = 70,000
Find the value of the expression.
Question 17.
105
Answer:
105=1,00,000
Question 18.
8 × 101
Answer:
8 × 101= 8 x 10 = 80
Question 19.
7 × 104
Answer:
7 × 104 = 7 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10= 70,000
Question 20.
3 × 105
Answer:
3 × 105 = 3 X 10 X 10 X 10 X 10 X 10=3,00,000
Rewrite the number as a whole number multiplied by a power of 10.
Question 21.
5,000
Answer:
5,000= 5 X 103
Question 22.
600,000
Answer:
6,00,000= 6 X 105
Question 23.
90
Answer:
90= 90 X 101
1.4 Decimals to Thousandths
Write the decimal as a fraction.
Question 24.
0.062
Answer:
0.062= 62 X 1/1,000
Question 25.
0.008
Answer:
0.008= 8 X 1/1,000
Question 26.
0.195
Answer:
0.195= 195 X 1/1,000
Write the fraction as a decimal.
Question 27.
\(\frac{2}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{1,000}\) = 2 x 1/1,000= 0.002
Question 28.
\(\frac{37}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{37}{1,000}\) = 37 x 1/1,000= 0.037
Question 29.
\(\frac{409}{1,000}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{409}{1,000}\)= 409/1,000=0.409
Question 30.
0.0.7 is 10 times as great as what number?
Answer:
0.07 is 10 times great as 0.007
Question 31.
0.04 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of what number?
Answer:
0.04 is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 0.4
1.5 Place Value with Decimals
Write the number in two other forms.
Question 32.
Standard form:
Word form:
Expanded form: 5 × 1 + 3 × \(\frac{1}{10}\) + 8 × \(\frac{1}{100}\) + 4 × \(\frac{1}{1,000}\)
Answer:
Standard form:5+0.3+0.08+0.004=5.384
Word form: five and three tenths, eight hundredths and 4 thousandths
Question 33.
Standard form: 2.059
Word form:
Expanded form:
Answer:
Word form: two and five hundredths and nine thousandths
Expanded form: 2 x 1 + 5 x 1/100 + 9 x 1/1000
Question 34.
Compare the values of the 5s in the number 1.055.
Answer:
5s value is at hundredths and another 5s value is at thousandths place
Question 35.
Compare the values of the 8s in the number 6.884.
Answer:
8s place value is at tenths value and other 8s place value is at hundredths place
1.6 Compare Decimals
Compare.
Question 36.
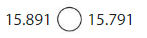
Answer:
15.891 > 15.791
the 8 value at tenths place is greater than 7 at tenths place
Question 37.

Answer:
8.205 < 8.250
the 0 at hundredths is less than 5 at hundredths
Question 38.

Answer:
Both are same
3.600 = 3.6
Order the decimals from least to greatest.
Question 39.
7.008, 7.09, 7.180
Answer:
7.008<7.09
7.09 <7.18
so the decimals from least to greatest are 7.008 , 7.09, 7.180
Question 40.
50.426, 50.42, 50
Answer:
50 < 50.42
50.42 < 50.426
so the decimals from least to greatest are 50, 50.42, 5.0426
Question 41.
Modeling Real Life
Newton weighs a treat at the pet store. He says it weighs less than 0.519 ounce but more than 0.453 ounce. Which treats could he have weighed?

Answer:
Newton says it weighs less than 0.519 ounce but more than 0.453 ounce,
so Blue berry waffle 0.512 which is in between 0.453<0.512<0.519
and We have more than 0.453 is 0.459 ounce which is Peanut butter and is less than 0.519 ounce
So Peanut butter 0.453 is in between 0.453<0.459<0.519
so newton would have weighed Peanut butter 0.459 ounce
and it can be even Blueberry waffle 0.512 ounce
newton’s treats could be Peanut butter ,Blueberry waffle
1.7 Round Decimals
Round the number to the place of the underlined digit.
Question 42.
9.514
Answer:
if 9 is digit then it is rounded as 9.0
if 5 then it is rounded as 9.500
if 1 then it is rounded as 9.520
if 4 then it is rounded as 9.520,9.510
Question 43.
1.027
Answer:
1.027 at 2 it is rounded as 1.03
Question 44.
8.469
Answer:
8.469, 8 is rounded as 8.500 or 8 or 8.000
Question 45.
32.501
Answer:
in 32.501
3 is rounded as 30.000
2- 33.000
5- 32.6 or 33
0-32.5
1 -32.500
Question 46.
Round 0.176 to the nearest
Answer:
0.200
Question 47.
Round 6.538 to the nearest tenth. hundredth.
Answer:
6.500
Question 48.
Round 7.425.
Nearest whole number:
Nearest tenth:
Nearest hundredth:
Answer:
Nearest whole number:8.000, 8
Nearest tenth:7.500
Nearest hundredth:7.430
Question 49.
Round 2.108.
Nearest whole number:
Nearest tenth:
Nearest hundredth:
Answer:
Nearest whole number:2.000, 2
Nearest tenth:2.100
Nearest hundredth:2.100
Final Words:
It is very important for the students to understand and learn the fundamentals at the primary level itself. Here we have prepared the questions as per the latest edition 2019. Keep the textbook aside and try to solve the problems by referring to our Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts. To make you comfortable we have provided the solution key for Big Ideas Math Grade 5 Chapter 1 Place Value Concepts in the pdf format. Stay tuned to our CCSS Math Answers to get the latest updates of BIM Grade 5 Chapters.
HDFCLIFE Pivot Calculator







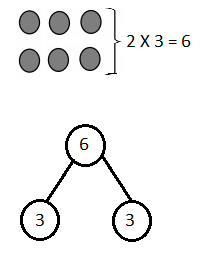
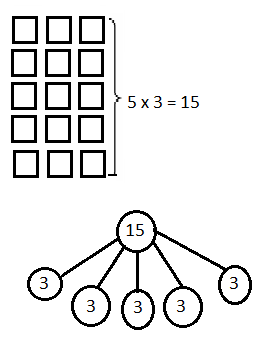


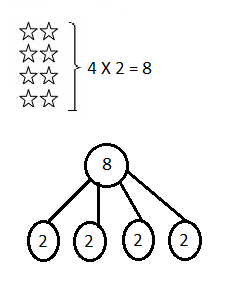















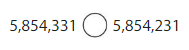







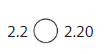









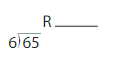
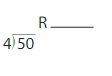





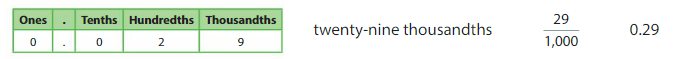





















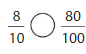
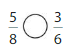
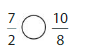











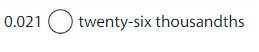
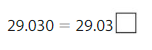
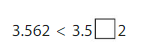

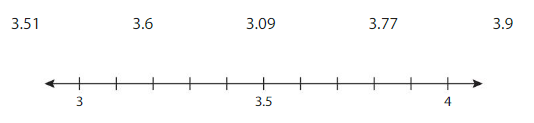
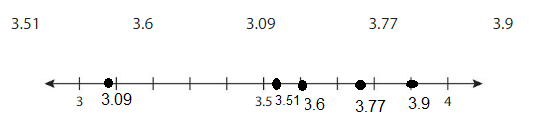







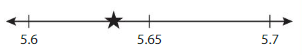








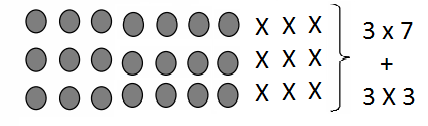
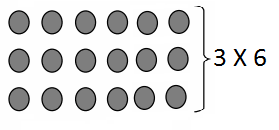
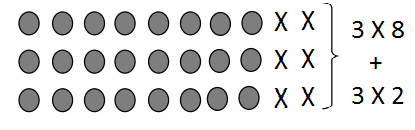

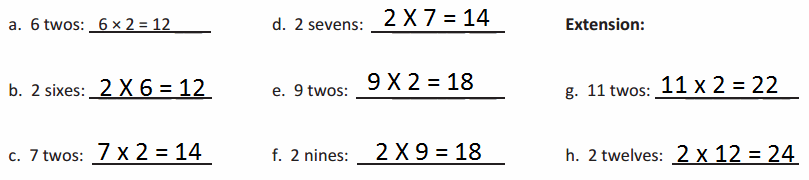 Explanation:
Explanation:
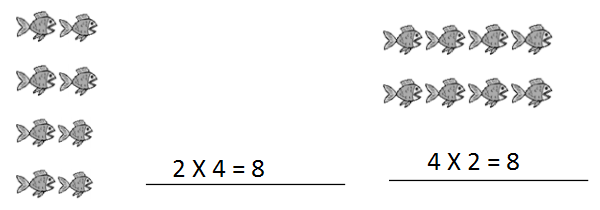 Explanation:
Explanation: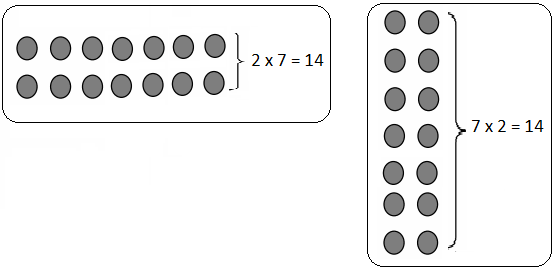
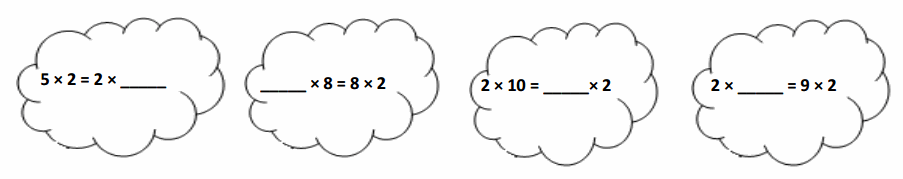
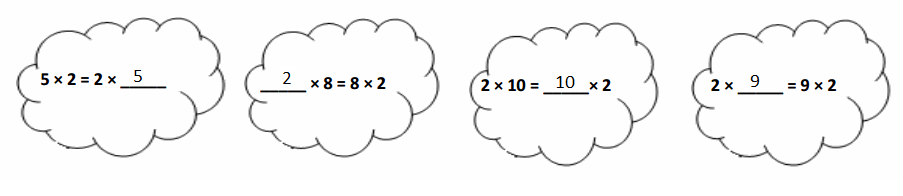
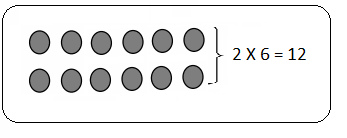
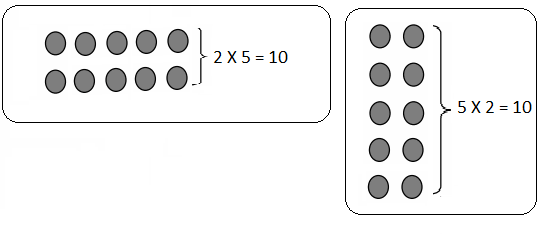
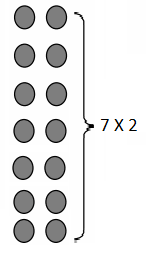

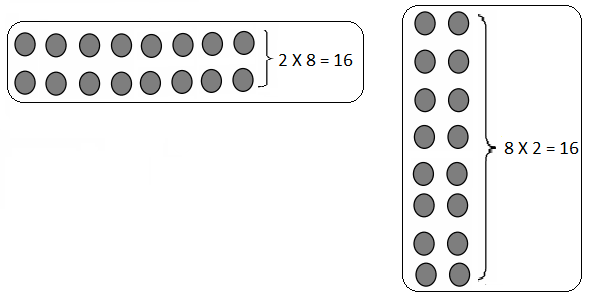
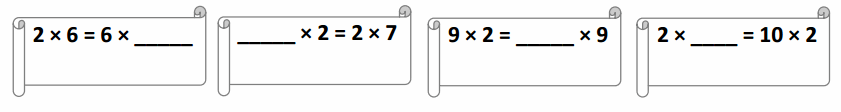
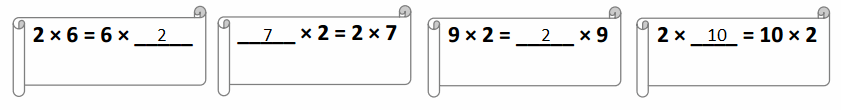
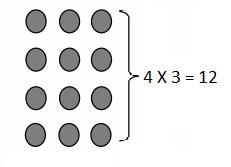
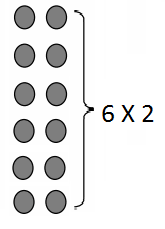

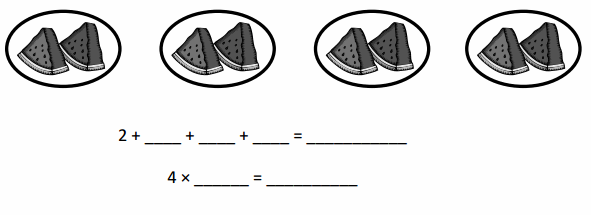
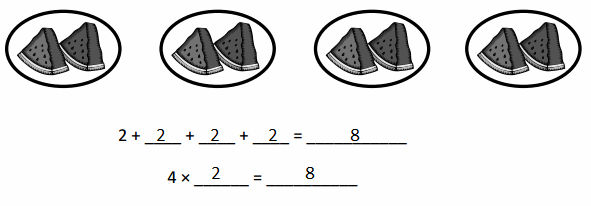
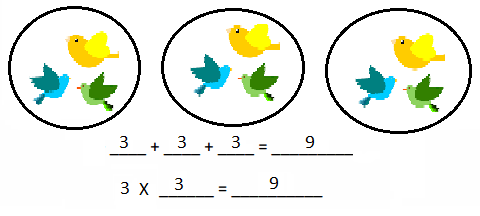



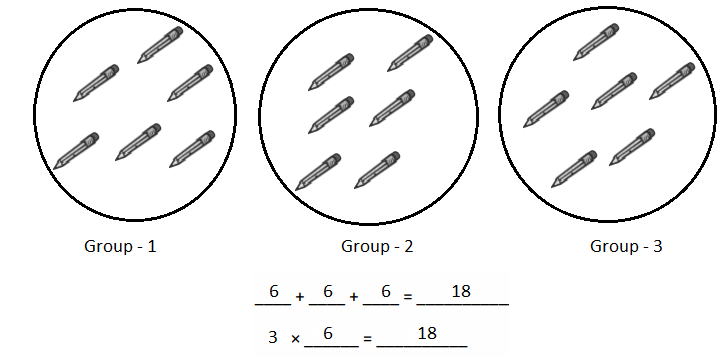






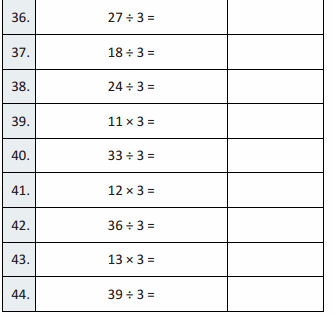
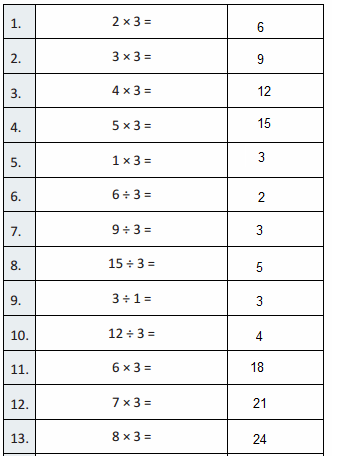
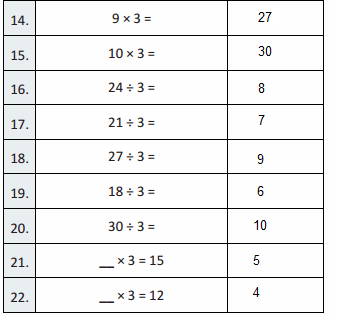
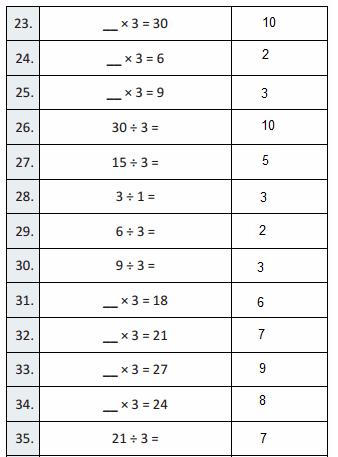
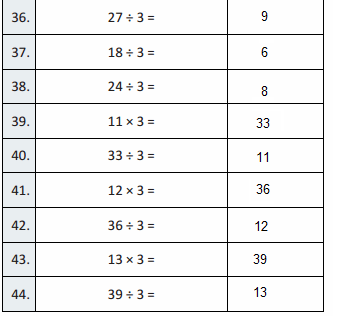
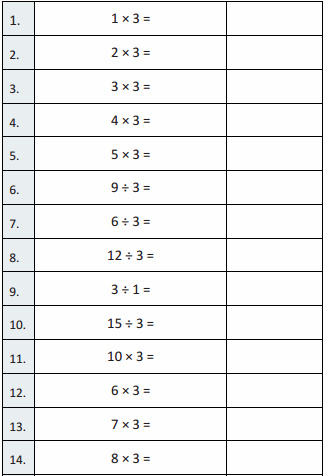
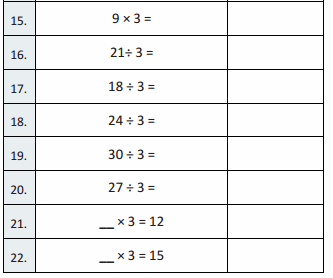
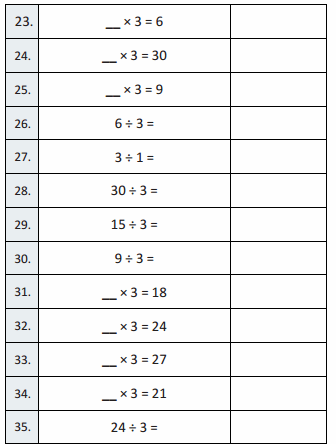

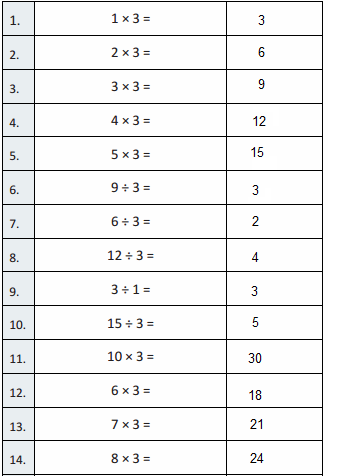
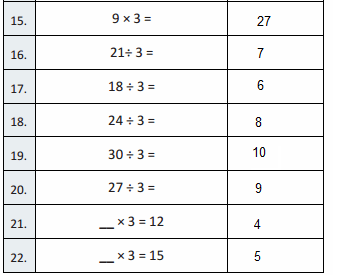
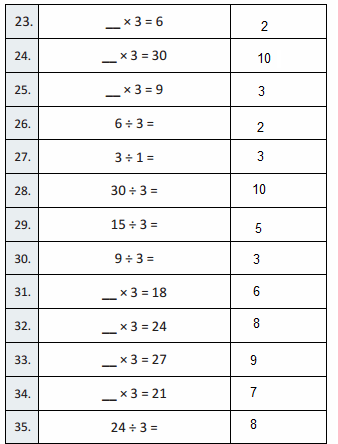
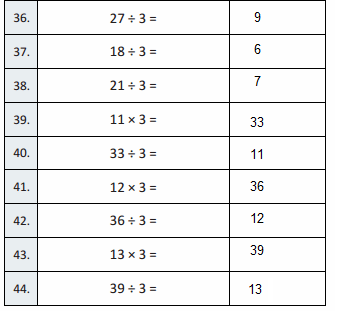



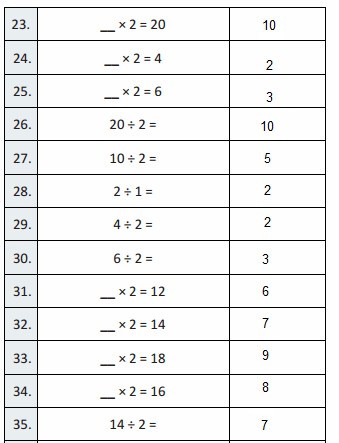
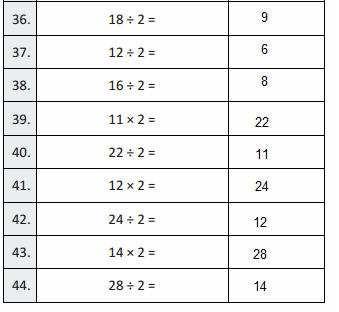
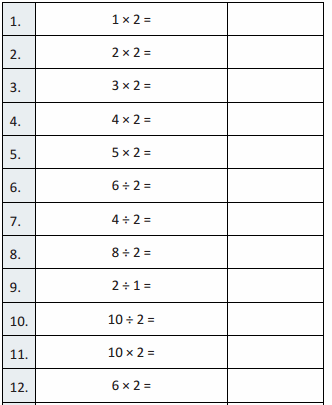
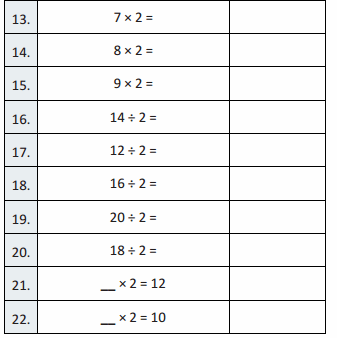
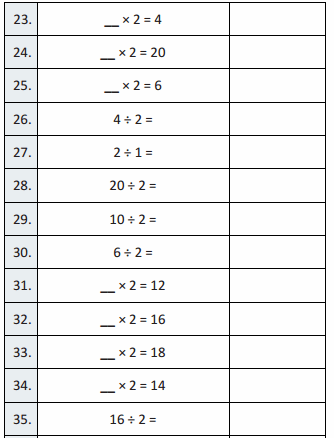
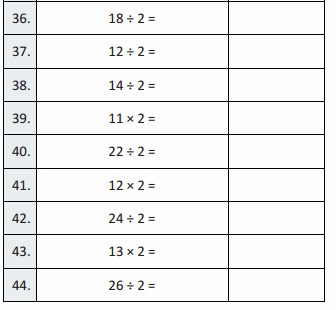
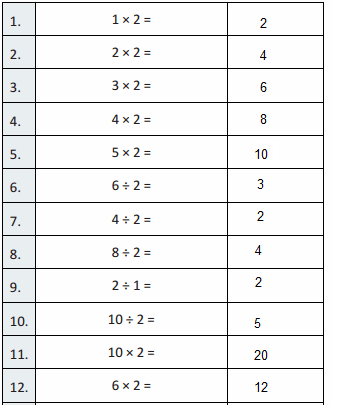
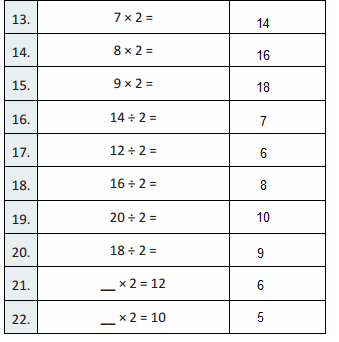
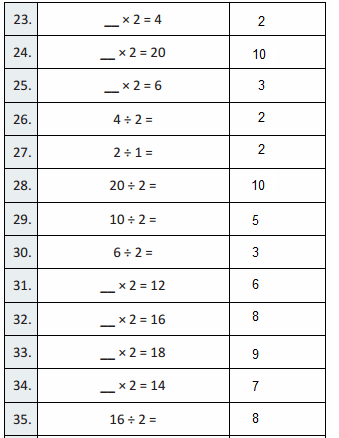
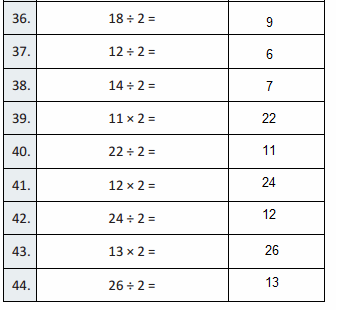
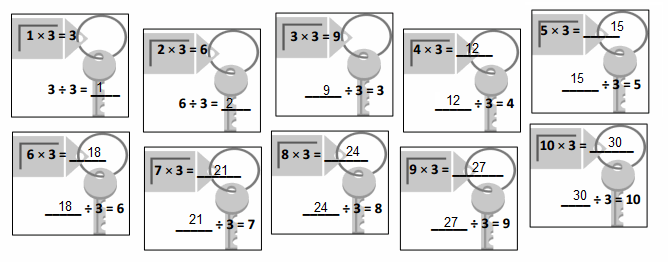 Explanation:
Explanation:
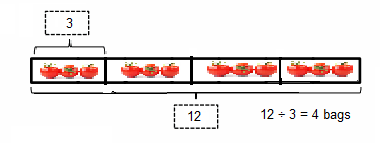
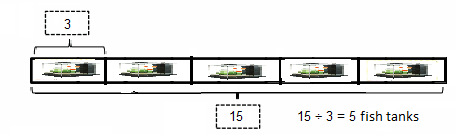

 Explanation:
Explanation:
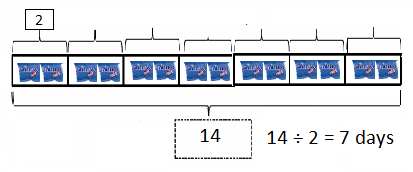
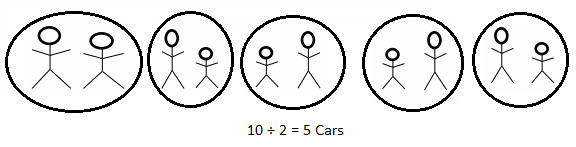
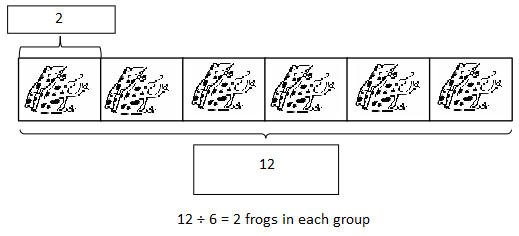
 Explanation:
Explanation: