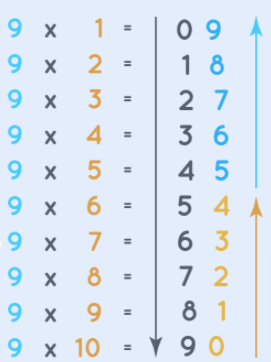
Table of 9 shows the results of adding 9 repetitively. Learning the 9 Times Table is quite necessary as without this primary knowledge you might feel the concepts of math more challenging to understand. One interesting fact about the Multiplication Table of 9 is that you get the next multiples of 9 by increasing the tens digit and decreasing the first digit at every step.
Math Tables makes it easy for you to perform quick calculations in mathematics. Go through the entire article to learn about the Tips & Tricks to Memorize the Multiplication Table of Nine, How to Read and Write the Table of 9. Download the Printable Multiplication Chart of 9 for free from here and take your preparation to next level.
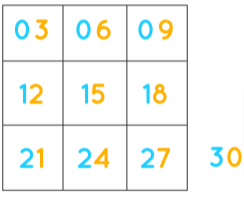
9 Times Multiplication Chart
We have provided Table of 9 in image format here. You can use this Multiplication Table of 9 Chart as a quick reference and download the image for free and resolve your queries. Students can recite it regularly and try to memorize it so as to apply these fundamentals in learning higher concepts in the mere future. You can stick this Multiplication Chart of 9 on your walls so that you can read them before you go to bed daily.

How to Read 9 Times Table?
Know how to read the Table of Nine orally by having a glance at the below modules. They are in the following fashion
One time nine is 9
Two times nine is 18
Three times nine is 27
Four times nine is 36
Five times nine is 45
Six times nine is 54
Seven times nine is 63
Eight times nine is 72
Nine times nine is 81
Ten times nine is 90
Eleven times nine is 99
Twelve times nine is 108
Nine Times Multiplication Table up to 20 | How to write a Multiplication Table of Nine?
Referring to Table of 9 you can learn multiplication facts about the table easily. Here, we have provided the Nine Times Table up to 20 numbers. You can use Table of 9 to perform mental math calculations right in your head. Enhance your problem-solving skills and speed of solving problems in your competitive exams by applying this knowledge. Also, learn how to write the Nine Times Multiplication Table by checking the table provided in tabular format.
| 9 | X | 1 | = | 9 |
| 9 | X | 2 | = | 18 |
| 9 | X | 3 | = | 27 |
| 9 | X | 4 | = | 36 |
| 9 | X | 5 | = | 45 |
| 9 | X | 6 | = | 54 |
| 9 | X | 7 | = | 63 |
| 9 | X | 8 | = | 72 |
| 9 | X | 9 | = | 81 |
| 9 | X | 10 | = | 90 |
| 9 | X | 11 | = | 99 |
| 9 | X | 12 | = | 108 |
| 9 | X | 13 | = | 117 |
| 9 | X | 14 | = | 126 |
| 9 | X | 15 | = | 135 |
| 9 | X | 16 | = | 144 |
| 9 | X | 17 | = | 153 |
| 9 | X | 18 | = | 162 |
| 9 | X | 19 | = | 171 |
| 9 | X | 20 | = | 180 |
Importance of Multiplication Table of Nine?
In general, Multiplication Table is obtained by multiplying the number 9 with all natural numbers. Refer to the following modules to know the importance of it. They are in the following fashion
- You can Identify the Patterns of Multiples easily.
- Furthermore, learning the Nine Times Multiplication Table helps you to solve problems on long division, multiplication, HCF, LCM problems easily.
- Memorizing the Nine Table you can enhance your speed of solving mathematical problems.
Tips for Learning 9 Times Table
In the below image you can notice the digits in one’s place reduce by 1 and while going from top to bottom. On the other hand, the digits in the tens place increase by 1 from top to bottom. If you keep these points in mind the Multiplication Table of 9 is quite simple to remember.
Get More Math Tables:
Solved Examples involving Table of Nine
1. Using the table of 9, evaluate 9 times 5 minus 3?
Solution:
Let us write 9 times 5 minus 3 mathematically
= 9*5-3
= 45-3
= 42
Thus, 9 times 5 minus 3 is 42
2. Mihir buys 9 packets of 14 pencils each. Using 9 times table find how many pencils has he bought in total?
Solution:
No. of Packets Mihir Bought = 9
No. of Pencils in each packet = 14
Number of Pencils Mihir bough in total = 9*14
= 126
Therefore, Mihir bought 126 pencils in total.
3. Using the table of 9, check whether 9 times 4 minus 9 is 27?
Solution:
Let us put the given statement in the form of a mathematical expression
= 9*4-9
= 36-9
= 27